Workspace Configuration Settings
|
Topics: |
You can set a variety of general parameters from the Workspace folder in the navigation pane. The parameters are available from a right-click menu and from options on the ribbon, organized under the following categories:
- Notification
- Settings
- License
These settings are saved in the appropriate configuration files.
Tip: If you prefer, you can edit these parameters directly in the associated configuration files. To do so, click Workspace on the sidebar. In the resources tree, expand Configuration Files, and choose the option that opens the file you wish to edit in a text editor. For details, see Editing Configuration Files.
You can monitor and troubleshoot server activity from Workspace in the resources tree. These functions are available from a right-click menu and from options on the ribbon, organized under the following categories:
- Monitor
- Status. See Monitoring Server Status.
- Data Service Agents. See Displaying and Customizing a Data Service Agents Page.
- Data Service Statistics. See Displaying Status Statistics and Aggregated Statistics for Data Services.
- Scheduler Agents. See Displaying and Customizing a Data Service Agents Page.
- Web Sessions. See Web Sessions.
- Live Console. See How to Display the Live EDAPRINT Log File.
- Diagnostic
- Savediag - Report a Bug. See Gathering Diagnostic Information for Customer Support Services.
- Download. See Analyzing Server Activity and Tracing Server Activity.
Workspace SET
|
Reference: |
The Workspace SET option lets you configure SMTP Server settings, Profile settings, Application settings, and Miscellaneous settings.
Reference: SMTP Server Settings
You can specify an IP address for the email server and a sender address. If the server is secured, you can specify the credentials for connecting to the server. You can also test your email connection from the E-mail Settings pane.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar. Click Settings, point to Workspace SET, and click SMTP Server Settings.
The E-Mail SMTP Server page opens, as shown in the following image.

The following settings are saved in the odin.cfg file:
- smtp_host
-
Indicates the IP address of the SMTP email server using the notation that is supported for your IP version (for example, for IPv4, use base 256 standard dot notation. When IPv6 is supported on a platform, and enabled, you can use either 256 standard dot notation or IPv6 notation.)
- port
-
Indicates the TCP port number that a client is connecting to. The default value is 25.
- smtp_user
-
Is the user ID to authorize access to the SMTP server.
- smtp_password
-
Is the password for the smtp_user.
- sender_email
-
Is the sender email address (the address that appears in the From field in emails).
- server_admin_email
-
Is a list that can consist of email addresses, user IDs and procedure names (for example, %myfex.fex), each on a separate line, with no delimiters.
Note: If email send operations fail, verify that the smtp host is active and/or that a virus scanner is not blocking edachkup.
When you have completed your entries, optionally click the Send Test E-mail button to test your connection, then click Save and Restart Server.
Reference: Profile Settings
You can control aspects of profile execution from the Profile Settings pane.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar. From the ribbon, click Settings, point to Workspace SET, and click Profile Settings.
The Profile Settings pane opens, as shown in the following image.
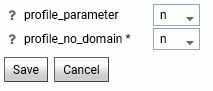
The following Profile Settings are saved in the edaserv.cfg file:
- profile_parameter
-
By passing parameters to profiles, you can submit different session parameters at different connection times. When this parameter is activated, any unresolved variables are prompted for during your initial logon to the Web Console.
Available settings are y and n.
If the server, user, or group profiles contain any unresolved variables, set the profile parameter keyword to y. The default setting is n.
- profile_no_domain *
-
In the Windows Server, to control whether the domain name is included in or excluded from a user profile name, choose:
n to add the domain name to the profile name (for example, user ibi/edaport becomes ibi_edaport.prf). N is the default value.
y to omit the domain name from the profile name (for example, user ibi/edaport becomes edaport.prf). This setting is required for compatibility with earlier releases of the Server.
Note: The y setting can be safely employed if a single domain is in use and there are no local user IDs that could interfere with domain IDs. If there is potential for interference between local user IDs and domain IDs that are connected to the server, the n setting is required to ensure that each user has a unique profile name.
Note that server must be restarted when this parameter is changed.
When you have completed your entries, click Save.
Reference: Application Settings
When you want to be able to reuse data within the same browser session, you can store the data in the form of a HOLD, SAVE, or SAVB file in the foccache directory, which is automatically created when the connection to the server is established. This becomes the first directory in the application path.
As long as the browser session remains active, the stored files remain in the foccache directory and can be referenced in requests using standard two part names. For example, the first request below creates a HOLD file in foccache, which is referenced by the second request:
TABLE FILE CAR PRINT CAR ON TABLE HOLD AS FOCCACHE/myfile END
TABLE FILE FOCCACHE/myfile PRINT * END
When the maximum foccache retention time is reached (180 minutes by default), the foccache directory is removed by the server and can no longer be referenced.
This feature provides an important mechanism for caching and running multiple instances of WebFOCUS active and drill-down reports. You can use any WebFOCUS graphical tool to create the request and generate a report.
Note: Each time a WebFOCUS user logs into the Managed Reporting (MR) environment, a new session with its own foccache directory is created. Files that were stored in a prior foccache directory are no longer accessible. When the user logs out of MR the foccache directory used within that MR session is no longer accessible.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar. From the ribbon, click Settings, point to Workspace SET, and click Application Settings.
The Application Settings pane opens, as shown in the following image.
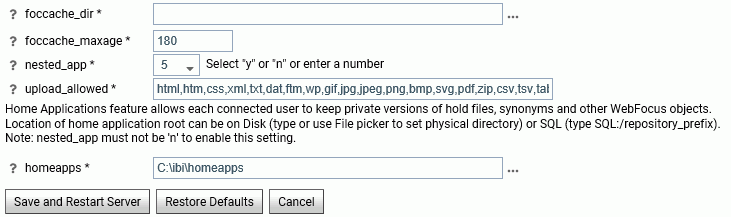
The following Application Settings are saved in the edaserve.cfg file.
- foccache_dir
-
Defines the location of the foccache directory. The default is edatemp/foccache/....
- foccache_maxage
-
Defines the maximum number of minutes that a foccache directory will last. The default is 180 minutes. When the foccache directory expires, the session also expires.
0 means unlimited (that is, the directory will be remain active as long as the session lasts or the server is running).
- nested_app
-
For applications containing subfolders or multiple-level subfolder trees, this parameter controls whether subfolders will be automatically added to the application path.
The valid values are:
- A positive integer - Enable nested application, and only a specific number of subfolder levels in the active application path.
- n - Disables nested applications. Only applications explicitly in the APP PATH will be used.
- y - Enables nested applications. The entire application subfolder tree under each application in the APP PATH is included into active application path.
The default value is 5.
Note: For z/OS servers, this setting is only applicable to directory-style applications, it is not applicable to PDS-style applications nor to applications mapped as a collection of ddnames.
- homeapps
-
If nested_app is set to y or a number, homeapps defines the location of the home application root directory. With homeapps defined, each connected user will see a My Home applications folder on the Application tree. Users can create new applications (home applications) in this folder. These applications will be visible and available only to the connected user and the server administrator. The user will have full access to his home applications.
Note: Only available with a DataMigrator or Managed Reporting license. A WebFOCUS Reporting Server requires a homeapps license to enable home applications.
- upload_allowed
-
Lists the extensions allowed for upload. You can remove extensions from the list to prevent files with those extensions from being uploaded.
When you have completed your entries, click Save and Restart Server.
Reference: Miscellaneous Settings
|
How to: |
Miscellaneous Settings allow you to set additional Workspace operating parameters, including automatic recovery, transaction coordination, soft and hard kill delays, maximum session log rows, time window for running response time averages, and proxy server settings.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar. From the ribbon, click Settings, point to Workspace SET, and click Miscellaneous Settings.
The Miscellaneous Settings pane opens, as shown in the following image.
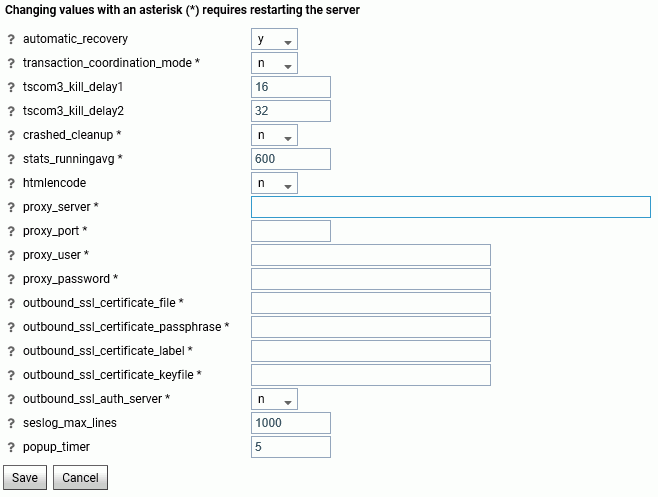
The following Miscellaneous Settings are saved in the edaserv.cfg file:
- automatic_recovery
-
Determines whether the server will automatically recover crashed listeners and/or special services. The default is n.
- transaction_coordination_mode
-
Selecting y, activates the iWay Transaction Coordinator. A Two-Phase Commit will be used when XA-Compliant databases participate in a transaction. The default is n.
- tscom3_kill_delay1
-
Defines the time (in seconds) allowed for an agent to stop before soft kill is sent. The default is 16.
- tscom3_kill_delay2
-
Defines the time (in seconds) allowed for a soft kill to work before a hard kill is sent. The default is 32.
- crashed_cleanup
-
By default, crashed agents are kept in the agents table for diagnostics purposes, and are only removed when they are explicitly killed. When this set to y, crashed agents are automatically removed from agents list when the Workspace Manager detects a crash. The default value is n.
- crashed_max_dump
-
If crashed_cleanup is set to y, this determines the number of memory dump files retained for later diagnosis.
- stats_runningavg
-
Defines the time window in seconds for the calculation of running response time averages. The default is 600.
- htmlencode
-
Specifies whether to encode HTML tags in data as plain text in order to prevent attacks by inserting executable code into data. Valid values are y and n. The default value is n.
- proxy_server
-
Defines a proxy server, which acts as an intermediary on requests for resources from other servers.
- proxy_port
-
Defines the port number of the proxy server.
- proxy_user
-
Defines a user ID for the proxy server.
- proxy_password
-
Defines a password for the user ID connecting to the proxy server.
- outbound_ssl_certificate_file
-
Required for SSL when using self-signed certificates on i5 systems.
- outbound_ssl_certificate_passphrase
-
Required for SSL when using self-signed certificates on i5 systems.
- outbound_ssl_certificate_label
-
Required for SSL when using self-signed certificates on i5 systems.
- outbound_ssl_certificate_keyfile
-
Required for SSL when using self-signed certificates on i5 systems.
- outbound_ssl_auth_server
-
Required for SSL when using self-signed certificates on i5 systems.
- seslog_max_lines
-
Defines the upper limit for the number of rows in a session log. When the limit is exceeded, only the latest records will be kept in the session log and the number of records will equal the limit. The default is 1000.
- popup_timer
-
Defines the time in seconds to wait before the popup timer appears. The default is 5.
z/OS Specific Parameters
- tmpalloc_primary
- tmpalloc_secondary
-
Allocation (in CYLs) for temporary Web Console files allocated by the HTTP listener. The default is 5 and 50, respectively.
- submit_opt
-
Customizes the call of the IKJEFF10 exit when submitting jobs with the DYNAM SUBMIT command.
- smf_recno
-
Defines the SMF record number that the server will use to record utilization statistics.
- smf_subtype
-
Defines which pairs of SMF subtype records are cut. The options are:
- all. Cut all records. This is the default.
- logon. Cut logon/logoff subtype only.
- query. Cut query begin/query end subtype only.
- privatedd
-
Defines how server will handle allocations for duplicated ddnames (same ddname allocated both to IRUNJCL and from a customer application using DYNAM) and what the search strategy will be.
When you have completed your entries, click Save.
Reference: Customize the IKJEFF10 Exit for DYNAM SUBMIT From the Web Console (z/OS)
To change how the server calls the IKJEFF10 exit, set the submit_opt parameter as follows:
- From the sidebar, click Workspace.
- From the
ribbon, click Worksapce Settings, and click Miscellaneous
Settings, or right-click Workspace on the resources tree, point to Settings,
and click Miscellaneous Settings.
The Miscellaneous Settings page opens.
- For the
submit_opt option, assign a separate value (0 or 1) in each of the
three drop-down lists. The default is 000.
The first drop-down list enables the call to IKJEFF10 from DYNAM SUBMIT. By default, the call is disabled.
- 0
-
Does not call IKJEFF10. This is the default setting.
- 1
-
Calls IKJEFF10.
The second drop-down list specifies that SUBMIT is to call IKJEFF10 in problem state, not in supervisor state. The IBM specification for IKJEFF10 requires supervisor state. If the version of IKJEFF10 in use at your site is capable of running in problem state, this option may be changed, thus allowing DYNAM SUBMIT to be used with IKJEFF10 when the server is not running APF-authorized. When you set:
- 0
-
Supervisor state is required for calling IKJEFF10. This is the default setting.
- 1
-
Supervisor state is not required to call IKJEFF10.
The third drop-down list allows SUBMIT to continue in the event that an error occurs while processing an in-stream data set. In-stream data sets are created by the following statements in the job:
//ddname DD * //ddname DD DATA /*XMIT //name XMIT /*DATASET
If an error is found in one of the previous statements (for example, a syntax error in the DLM parameter), the SUBMIT operation is normally cancelled. This option allows submission of the job to continue, although in such a case the results are unpredictable since the JCL contained within the in-stream data set may be erroneously interpreted as part of the job being submitted.
- 0
-
Terminates SUBMIT on in-stream data set error. This is the default setting.
- 1
-
Does not terminate SUBMIT on in-stream data set error.
- Click Save.
Your entries are registered in the edaserve.cfg file.
Notification
|
Topics: |
|
How to: |
Event Routing and a customized Login Message can be configured from the Notification menu on the Workspace ribbon.
Event Routing allows you to launch procedures or send email based on different server events (agent or listener crashes, server configuration errors, disk space limitations, and others). All events are classified by type as information, warning, or error. These can be pre-defined or custom-defined events.
The Event Routing page shows the Default and Customized Event Routing.
The Default routings are shown in the following image.
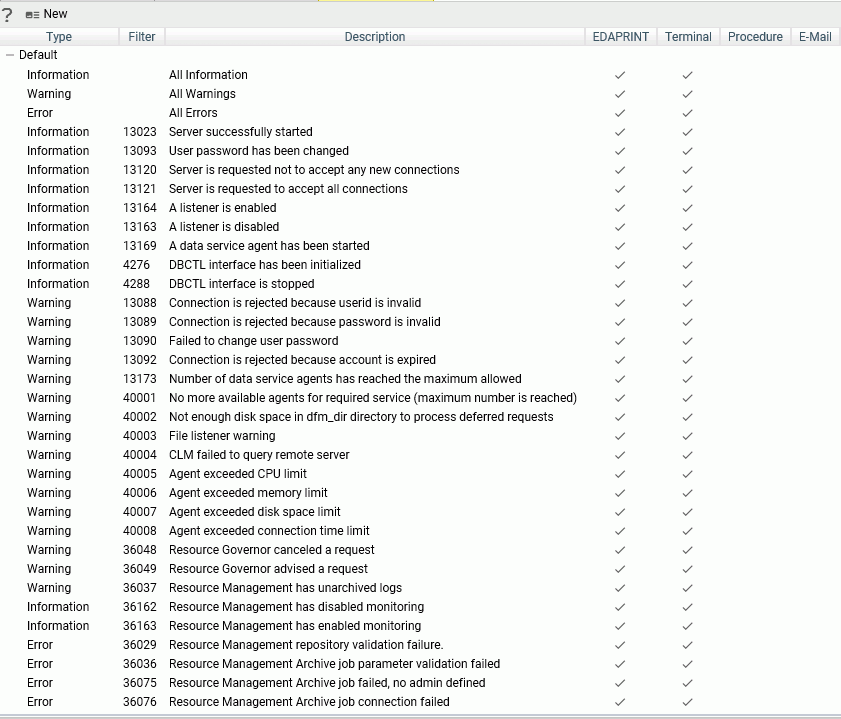
Procedure: How to Customize an Event Routing
By customizing event routing, you can launch a procedure or send email based on server events.
For each event, you can also select whether to write the event to the EDAPRINT log or the terminal.
- From the sidebar, click Workspace.
- From the ribbon, click Notification, then Event Routing.
- Right-click an event and click Customize Event Routing, or click New on the menu bar.
The Customize Event Routing page opens, as shown in the following image.
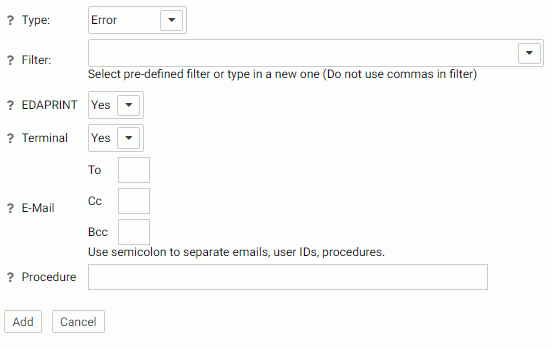
- From the Type drop-down menu, select a message type. The choices are Information, Error, Warning, and Any.
- Enter the event criteria in the Filter field, or select a predefined event from the drop-down menu.
- From the
EDAPRINT drop-down menu, select Yes if you
want to write the selected event message to the server log.
In z/OS, the selected server messages can be also written to the z/OS system log by selecting Yes from the JESLOG drop-down menu.
- From the Terminal drop-down menu, select Yes if you want to write the selected event message to the terminal.
- Optionally, enter email addresses to send an email when the event occurs.
- Optionally, enter a procedure to execute in the Procedure field, including the application name, for example, utility/movefiles.
- Click Add for a new event, or Change for an existing event.
The event is added to the Customize Event Routing Page.
- Click Save and Restart Server.
Example: Suppressing an EDAPRINT Log Message
This example shows how to suppress the following EDAPRINT log message by customizing an event routing:
request by edapsmr to expire foccache session
- Open the Event Routing page.
- Select Warning from the Type drop-down list.
- Enter the following event in the Filter text box:
request by edapsmr to expire foccache session
- Select No from the EDAPRINT and Terminal drop-down lists.
- Leave the E-Mail parameters blank, so that an email will not be sent when the event occurs.
- Click Add. The event is added, but not yet saved.
- Click Save and Restart.
When the server restarts, this custom event will suppress the request by edapsmr to expire foccache session message in the edaprint.log file.
Procedure: How to Set Workspace Log Properties for Event Routing
The Workspace Log Properties page controls both event routing email and the edaprint log by allowing you to specify a suppression interval for email notifications from event routing, and to include a number of lines from the edaprint log file in the email body. The edaprint log file provides information about the events occurring on the server before a triggered event.
For information on the edaprint log, see How to Set Workspace Log Properties to Control the Edaprint Log.
- From the sidebar, click Workspace.
- Open Logs and Traces.
- Right-click Workspace
Logs and click Properties.
The Workspace Logs Properties page opens, as shown in the following image.
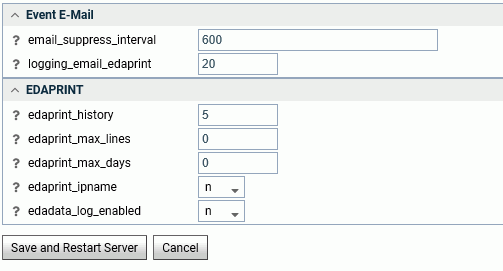
- Enter or
select values for the Event Email parameters.
The Event Email parameters are:
- email_suppress_interval
-
Suppresses duplicate email notifications if the same event occurs again during this time interval (in seconds). Zero disabled suppression. The default value is 600 (10 minutes).
- logging_email_edaprint
-
Defines the maximum number of server messages from edaprint.log are included in the email. The default value is 20.
- Click Save and Restart Server.
EVENT_TEXT and EVENT_ID
When a procedure is triggered by an event, the ID of the routing event and the text of the event message are automatically available to the procedure as the EVENT_ID and EVENT_TEXT parameters, respectively. The EVENT_TEXT parameter needs to be decrypted using the following user subroutine:
B64DECODE('XXXXXXXXXX', 'Ann');Locale Settings
|
Reference: |
The Web Console provides parameters that define locale-specific date, time, and currency formats as well as parameters for configuring National Language Support.
Reference: NLS Settings
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar or right-click Workspace on the resources tree. Then point ot Locale and click Configuration Wizard. The NLS Configuration Wizard opens, as shown in the following image.
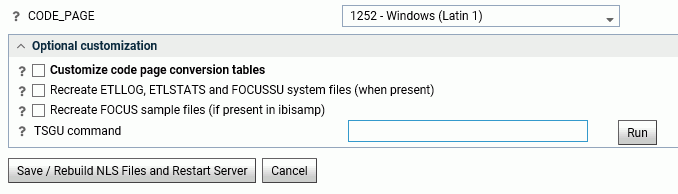
The following NLS settings are saved in the nlscfg.err file:
- CODE_PAGE
-
Is the code page of the data sources accessed by the server.
Select a code page from the drop-down list of supported code pages, including Unicode.
The default value is 1252 for Windows and UNIX, and 37 for IBM i (formerly known as i5/OS) and z/OS.
The current value of CODE_PAGE is available to applications as the &FOCCODEPAGE variable.
Optional customization
- Customize code page conversion tables
-
Select this check box to display a list of code pages and descriptions for the possible data sources accessed by the server or the client code page.
Several code pages are always selected by default and cannot be deselected. These are:
37 --IBM MF United States
137 --U.S. English/Western Europe (Latin 1)
437 --U.S. English
1047 --IBM MF Open Systems (Latin 1)
1252 --Windows Latin; 65001 --Unicode (UTF-8)
65001 Unicode (UTF-8)
65002 Unicode (UTF-EBCDIC)
Other code pages may also be selected by default, depending on the LANG attribute chosen.
The NLS Configuration Wizard creates conversion tables for these code pages to make them available for subsequent conversion.
Select any additional code pages for which you want tables to be created. For example, if you want to designate a particular code page to be generated in synonyms for flat (fixed) files or VSAM files, you must already have created a code page conversion table using the Customize code page conversion table option during NLS configuration.
- Recreate ETLLOG, ETLSTATS and FOCUSSU system files
-
Check this box if you wish to load FOCUS internal files in the server code page (as defined in the CODE_PAGE field).
This is recommended if the compatibility of the new and prior code pages is unknown.
- Recreate FOCUS sample files
-
Check this box if you wish to load the sample files (in the ibisamp application) in the server code page (as defined in the CODE_PAGE field).
- TSGU command
-
TSGU is a utility program to configure NLS settings. It is usually not required, but in the following cases it must be executed manually.
- To create PDFXTBL. When TYPE 1 fonts should be included
in PDF format file, the TYPE 1 font transcoding table must be generated
using the following syntax:
PDFX {font-name}
- To create PDFYTBL. When
Unicode fonts should be used in PDF format file, the special font
information tables (PDFYTBL) must be generated using the following
syntax:
KTBL {pdfy-name}
- To create PDFXTBL. When TYPE 1 fonts should be included
in PDF format file, the TYPE 1 font transcoding table must be generated
using the following syntax:
Complete the configuration, then click Save/Rebuild NLS Files and Restart Server. The server creates the necessary transcoding, sorting, and monocasing tables for the selected code page.
Reference: Locale Parameters
The Web Console provides parameters for configuring locale-based date, time, and currency parameters.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar or right-click Workspace on the resources tree. Then click Locale and select Locale (Language, Numbers, Currency, Dates). The Change Core Engine Settings in edasprof.prf page opens, as shown in the following image.
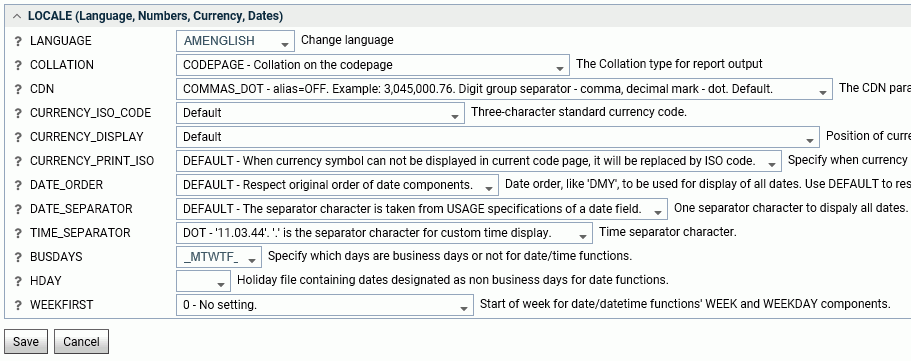
The following parameter values can be set and stored in edasprof.prf.
- LANGUAGE
-
Controls the default value of the code page, and the language of server error messages, if available in translation.
Choose a language name or abbreviation from the drop-down list.
The default value is AMENGLISH (American English) on all platforms.
Localized error message files exist for certain languages. If you choose a language for which localized error message files do not exist, the server messages and console appear in English. If you would like the messages and console to appear in a language for which the server has not been localized, you can provide translation yourself. To localize the console, translate the file wceng.lng and rename it to wcXXX.lng where 'XXX' is the three-letter language code for the server. For error messages, translate all or any relevant *.err files and append the same three-letter language code to it. All files are located in the \home\nls folder.
The current value of LANG is available to applications as the &FOCLANGCODE variable. However, it will be blank if it is not configured.
- COLLATION
-
Establishes a binary or case-insensitive collation sequence. The values are:
- CODEPAGE. Bases the collation sequence on the code page in effect. This is the default value.
- BINARY. Bases the collation sequence on binary values.
- SRV_CS. Bases the collation sequence on the LANGUAGE setting, and is case-sensitive.
- SRV_CI. Bases collation sequence on the LANGUAGE setting, and is case-insensitive.
When code page files are not modified, CODEPAGE is the same as BINARY, except for Danish, Finnish, German, Norwegian, or Swedish in EBCDIC environment.
The SET COLLATION command has the same effect, and overrides this default setting.
- CDN
-
Defines the punctuation symbols to be used for numbers. Valid values are:
- COMMAS_DOT. Uses a dot (.) as the decimal separator and comma (,) as the thousands separator. The alias is OFF. This is the default value.
- DOTS_COMMA. Uses a comma as the decimal separator and dot as the thousands separator. The alias is ON.
- SPACES_COMMA. Uses a comma as the decimal separator and space as the thousands separator. The alias is SPACE.
- SPACES_DOT. Uses a dot as the decimal separator and space as the thousands separator. The alias is SPACEP.
- QUOTES_COMMA. Uses a comma as the decimal separator and single quotation mark (') as the thousands separator. The alias is QUOTE.
- QUOTES_DOT. Uses a dot as the decimal separator and single quotation mark as the thousands separator. The alias is QUOTEP.
- CURRENCY_ISO_CODE
-
Is a standard three-character currency code such as USD for US Dollars or JPY for Japanese Yen. The default value is default, which uses the currency code for the configured language code.
- CURRENCY_DISPLAY
-
Defines the position of the currency symbol relative to a number. The default value is default, which uses the position for the format and currency symbol in effect. Valid values are:
- LEFT_FIXED. The currency symbol is left-justified preceding the number.
- LEFT_FIXED_SPACE. The currency symbol is left-justified preceding the number, with at least one space between the symbol and the number.
- LEFT_FLOAT. The currency symbol precedes the number, with no space between them.
- LEFT_FLOAT_SPACE. The currency symbol precedes the number, with one space between them.
- TRAILING. The currency symbol follows the number, with no space between them.
- TRAILING_SPACE. The currency symbol follows the number, with one space between them.
- CURRENCY_PRINT_ISO
-
Defines what will happen when the currency symbol cannot be displayed by the code page in effect. Valid values are:
- DEFAULT. Replaces the currency symbol with its ISO code, when the symbol cannot be displayed by the code page in effect. This is the default value.
- ALWAYS. Always replaces the currency symbol with its ISO code.
- NEVER. Never replaces the currency symbol with its ISO code. If the currency symbol cannot be displayed by the code page in effect, it will not be printed at all.
- DATE_ORDER
-
Defines the order of date components for display. Valid values are:
- DEFAULT. Respects the original order of date components. This is the default value.
- DMY. Displays all dates in day/month/year order.
- MDY. Displays all dates in month/day/year order.
- YMD. Displays all dates in year/month/day order.
- DATE_SEPARATOR
-
Defines the separator for date components for display. Valid values are:
- DEFAULT. Respects the separator defined by the USAGE format of the field.
- SLASH. Uses a slash (/) to separate date components.
- DASH. Uses a dash (-) to separate date components.
- BLANK. Uses a blank to separate date components.
- DOT. Uses a dot (.) to separate date components.
- NONE. Does not separate date components.
- TIME_SEPARATOR
-
Defines the separator for time components for the &TOD system variable. Valid values are:
- DOT. Uses a dot (.) to separate time components. This is the default value.
- COLON. Uses a colon (:) to separate time components.
- BUSDAYS
-
Defines which days are business days for date-time functions. The default value is _MTWTF_.
- HDAY
-
Specifies a holiday file for listing dates that are non-business days for use with date functions. The default value is OFF (no holiday file).
- WEEKFIRST
-
Defines the first day of the week for the WEEK and WEEKDAY components of date and date-time functions.
Reference: Font Support for Arabic and Thai PDF and PostScript Formats
Users that want to output Arabic characters in PDF or PostScript formats can select the Times New Roman font.
Users that want to output Thai characters in PDF or PostScript formats can select the Tahoma font.
Reference: Language and Default Code Pages for Windows and UNIX
This chart provides information generated by the ? LANG SET command from the Windows and UNIX platforms.
|
Language Code |
Language Name |
Language Abbreviation |
Language ID |
Code Page |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
001 |
AMENGLISH |
AME |
en |
1252 |
|
001 |
ENGLISH |
ENG |
en |
1252 |
|
020 |
ARABIC |
ARB |
ar |
1256 |
|
10351 |
B-PORTUGUESE |
BRA |
br |
1252 |
|
385 |
CROATIAN |
HRV |
hr |
1250 |
|
420 |
CZECH |
CZE |
cs |
1250 |
|
045 |
DANISH |
DAN |
da |
1252 |
|
031 |
DUTCH |
DUT |
nl |
1252 |
|
372 |
ESTONIAN |
EST |
et |
923 |
|
358 |
FINNISH |
FIN |
fi |
1252 |
|
033 |
FRENCH |
FRE |
fr |
1252 |
|
033 |
FRENCH |
FRE |
fc |
1252 |
|
049 |
GERMAN |
GER |
de |
1252 |
|
049 |
GERMAN |
GER |
at |
1252 |
|
030 |
GREEK |
GRE |
el |
1253 |
|
972 |
HEBREW |
HEB |
iw |
916 |
|
036 |
HUNGARIAN |
HUN |
hu |
1250 |
|
039 |
ITALIAN |
ITA |
it |
1252 |
|
081 |
JAPANESE |
JPN |
ja |
942 |
|
081 |
JAPANESE-EUC |
JPE |
je |
10942 |
|
082 |
KOREAN |
KOR |
ko |
949 |
|
371 |
LATVIAN |
LVA |
lv |
1257 |
|
370 |
LITHUANIAN |
LTU |
lt |
1257 |
|
047 |
NORWEGIAN |
NOR |
no |
1252 |
|
048 |
POLISH |
POL |
pl |
1250 |
|
351 |
PORTUGUESE |
POR |
pt |
1252 |
|
040 |
ROMANIAN |
ROM |
ro |
1250 |
|
007 |
RUSSIAN |
RUS |
ru |
1251 |
|
085 |
S-CHINESE |
PRC |
zh |
946 |
|
421 |
SLOVAK |
SVK |
sk |
1250 |
|
034 |
SPANISH |
SPA |
es |
1252 |
|
046 |
SWEDISH |
SWE |
sv |
1252 |
|
086 |
T-CHINESE |
ROC |
tw |
10948 |
|
066 |
THAI |
THA |
th |
874 |
|
090 |
TURKISH |
TUR |
tr |
920 |
|
044 |
UKENGLISH |
UKE |
uk |
1252 |
|
800 |
UNICODE |
UCS |
uc |
65001 |
Reference: Language and Default Code Pages for IBM i and z/OS
This chart provides information generated by the ? LANG SET command from the IBM i and z/OS platforms.
|
Language Code |
Language Name |
Language Abbreviation |
Language ID |
Code Page |
|---|---|---|---|---|
|
001 |
AMENGLISH |
AME |
en |
37 |
|
001 |
ENGLISH |
ENG |
en |
37 |
|
020 |
ARABIC |
ARB |
ar |
420 |
|
10351 |
B-PORTUGUESE |
BRA |
br |
37 |
|
420 |
CZECH |
CZE |
cz |
870 |
|
045 |
DANISH |
DAN |
da |
277 |
|
031 |
DUTCH |
DUT |
nl |
37 |
|
372 |
ESTONIAN |
EST |
et |
1112 |
|
358 |
FINNISH |
FIN |
fi |
278 |
|
033 |
FRENCH |
FRE |
fr |
297 |
|
033 |
FRENCH |
FRE |
fc |
297 |
|
049 |
GERMAN |
GER |
de |
273 |
|
049 |
GERMAN-500 |
GE5 |
at |
500 |
|
030 |
GREEK |
GRE |
el |
875 |
|
972 |
HEBREW |
HEB |
iw |
424 |
|
036 |
HUNGARIAN |
HUN |
hu |
870 |
|
039 |
ITALIAN |
ITA |
it |
280 |
|
081 |
JAPANESE |
JPN |
ja |
939 |
|
10081 |
JAPANESE-930 |
JPK |
jk |
930 |
|
082 |
KOREAN |
KOR |
ko |
933 |
|
371 |
LATVIAN |
LVA |
lv |
1112 |
|
370 |
LITHUANIAN |
LTU |
lt |
1112 |
|
047 |
NORWEGIAN |
NOR |
no |
277 |
|
048 |
POLISH |
POL |
pl |
870 |
|
351 |
PORTUGUESE |
POR |
pt |
37 |
|
040 |
ROMANIAN |
ROM |
ro |
870 |
|
007 |
RUSSIAN |
RUS |
ru |
1025 |
|
085 |
S-CHINESE |
PRC |
zh |
935 |
|
042 |
SLOVAK |
SVK |
sk |
870 |
|
034 |
SPANISH |
SPA |
es |
284 |
|
046 |
SWEDISH |
SWE |
sv |
278 |
|
086 |
T-CHINESE |
ROC |
tw |
937 |
|
066 |
THAI |
THA |
th |
838 |
|
090 |
TURKISH |
TUR |
tr |
1026 |
|
044 |
UKENGLISH |
UKE |
uk |
285 |
|
800 |
UNICODE |
UCS |
uc |
65002 |
Login Message
|
How to: |
Server administrators can customize the login and connection result screens with custom messages. The Login Message option is available from the Notification button on the ribbon.
Procedure: How to Customize the Login Screen With a Message
To customize the login screen:
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- From the ribbon, click Notification, then Login Message.
The Login Message page opens, as shown in the following image.
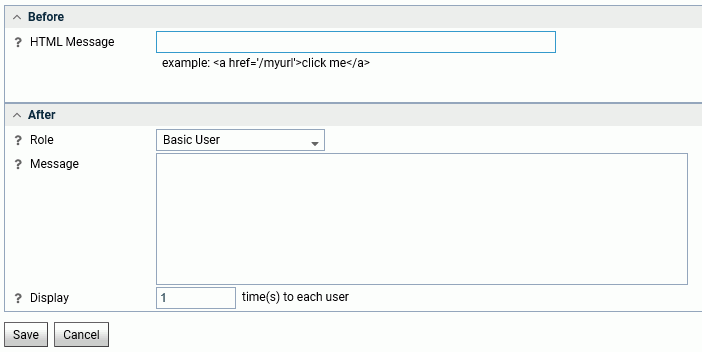
- Enter the message in the HTML Message field
in the Before section. It can have plain text as well as HTML tags.
For example, enter the following text.
For connection issues, contact Server Administration
- Click Save.
The message is added to the login page, as shown in the following image.
Procedure: How to Customize the Connection Result Screen With a Message
Server administrators can customize the connection result screen for each user type.
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- From the ribbon, click Notification then Login Message.
The Login Message page opens.
- Select a user type from the Role drop-down menu. The options are Server Administrator, Application Administrator, Server Operator, Basic User, and All Users.
- Enter the text of the message in the Message field of
the After field:
Please sign off by 6pm tonight.
Optionally, you can set the number of times the message will appear by entering a value in the Display field.
- Click Save.
The message is displayed after a successful connection, as shown in the following image.

Web Console Appearance
The Web Console appearance parameters control the look of the Web Console, as well as accessibility and menu bar customization.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar. From the ribbon, click Settings, then Web Console Appearance.
The Web Console Appearance page opens, as shown in the following image.
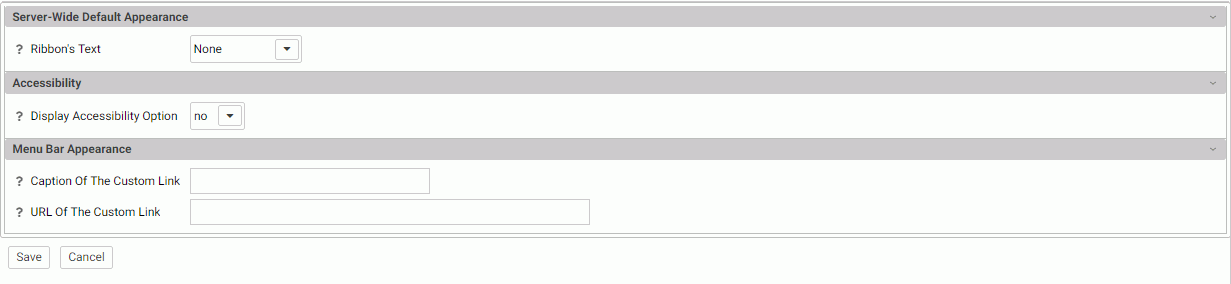
The following Web Console Appearance settings are saved in the edaserv.cfg file.
Server-Wide Default Appearance
- Ribbon's Text
-
Select from Icon Text Only or None. The default is None.
Accessibility
- Display Accessibility Option
-
Allows users to enable or disable an accessibility display.
Menu Bar Appearance
- Caption Of The Custom Link
-
Specifies the text of a custom link that is shown in the menu bar of the Web Console.
- URL Of The Custom Link
-
Specifies the URL of a custom link that is shown in the menu bar of the Web Console.
When you have completed your entries, click Save.
FOCUS Sets and Info
|
Topics: |
You can generate reports about many aspects of WebFOCUS processing using the Focus Sets and Info option on the Workspace Settings menu.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar. From the ribbon, click Settings, then Focus Sets and Info.
Core Engine Settings
Core engine settings allow you to control a wide range of services, including Dialogue Manager, LOCALE, StyleSheet, Common, TABLE, HLI, Tracing, and Other Sets.
To access the Core Engine settings:
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- From the ribbon, click Settings, point to FOCUS Sets and Info,
then click Core Engine Settings.
The Core Engine Settings pane opens, as shown in the following image.
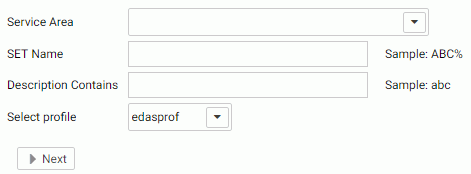
- Select one or more services from the Service Area list.
- Optionally, enter a string in the SET
Name field to find specific settings, using % as a wildcard.
For example, to find settings containing DATE, enter DATE%. All settings are upper case and the SET Name field is case sensitive.
- Optionally, enter a string in the Description Contains field to search for settings by their descriptions.
- Optionally, select a profile from the Select profile drop-down menu.
- Click Next.
The Core Engine Settings pane opens.
- Make your changes and click Save.
Core Engine System Variables
Core Engine System variables control the functionality of the server.
The variables fall into the following categories:
- Display Information
- Operating System
- Release Information
- National Language Support
- File Information
- Statistical Variables
- Date/Time Variables
- Security Information
- Miscellaneous System Variables
To view Core System variables:
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- On the ribbon, click Settings, point to FOCUS Sets and Info,
and click Core Engine System Variables.
The Core System Variable pane opens, as shown in the following image.

- Select one or more services from the Service Area list.
- Optionally, enter a string in the Variable Name field to find specific variables, using % as a wildcard. Variables are all upper case and all begin with an ampersand (&).
- Optionally, enter a string in the Description Contains field to search for variables by their descriptions.
- Click Next.
The Core System Variables are displayed.
Core Engine Global Variables
You can add global variables to a profile on the server to deliver default values or execute SET commands.
To create Core Engine global variables:
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- From the ribbon, click Settings, point to FOCUS Sets and Info,
and click Core Engine Global Variables.
The Core Engine Global Variable pane opens, as shown in the following image.

- Optionally, select a profile from the drop-down menu. The default is edaprof.
- Click Add New.
- On the Core Engine Global Variables pane, select SET or DEFAULT from the Command drop-down menu.
- Enter a name and expression for the variable in the corresponding
fields, as shown in the following image.
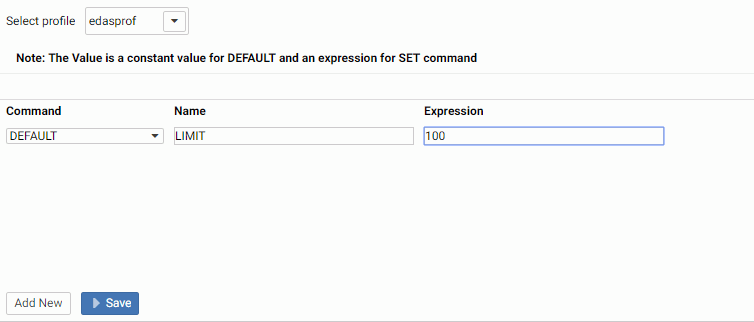
To add an additional global variable, click Add New.
- Click Save.
Displaying Settings for Web Console Preferences
To display or change the Web Console preferences, click Workspace on the sidebar. Click Settings on the ribbon, and click Settings for Web Console Preferences.
The Settings for Web Console Preferences page opens.
You can select a profile or procedure in which to save these settings. The default profile is edasprof.prf. You can set preferences for the following categories.
- Application Preferences. Lets you select values for the following options:
- Show File/Directory Caption Instead of Name. The default value is No.
- Show Files from Nested Applications. The default value is No.
- Show Also Applications not in APPPATH. The default value is No.
- Show Descriptions on Application Tree. The default value is No.
- Show edahome, edaconf, edaprfu, scaroot, edatemp, edalog and focchache. The default value is No.
- Show Files on File Panel. The default value is Yes. If you change this to No, files will be shown on the application tree when you open an application folder.
- Restrict Application Ribbon. The default value is On.
- Data Assist. You can select values for the following options:
- Initial value for 'Optimize Load' DM Flow Property. The default value is Off.
- Restrict Data Assist Menu. The default value is On.
- Auto-run for Synonym Editor. Default value is Run on Change.
- Auto-run for Test Query. Default value isRun on Change with Limited Data.
- Auto-run for Custom Copy. Default value is Do Not Run on Change.
- Auto-run for Upload. Default value is Run on Change.
- Auto show data in Synonym Editor tree. Default value is No.
- Auto show data in Test Query tree. Default value is No.
- Auto show data in Custom Copy tree. Default value is No.
- Auto show data in Upload tree. Default value is Yes.
- Enable Persistent Help. The default value is Yes.
- Display Function Strategy. The default value is Short Description. You can select Syntax to see the function syntax instead of the description.
- Display Name Strategy. The default value is Title. You can select Alias, Description, or Name.
- Undo Limit. The default value is 50.
- Aggregate Filter Type. The default value is WHERE_GROUPED. You can select WHERE TOTAL.
- Auto update related nodes. The default value is No.
- Use segment name to qualify field references. The default value is For duplicate fields only. You can select Always.
- Support extended options. Default value is No.
- BV_NAMESPACE value (ON/OFF) in Data Assist. The default value is OFF.
- Support Business Folders for Cube. The default value is Yes.
- Auto-run for Compound/Layout. Default value is Run on Change.
- Auto-run Data Profiling for Join. Default value is Yes.
- Show Filters and Groups in Modal Dialog. The default value is No.
- Data Assist Joins. You can select values for the following options.
- Insert child segments with snowflakes. Default value is No.
- Default Join Type. The default value is Multiple.
- Display full component names. Default value is Yes.
- Use application name to qualify synonym reference. Default Value is Yes.
- Data Flow Preferences.
- Use application directory name with flow components. Default value is Yes.
- Show Notes. Default value is No.
- Automatically select all columns. Default value is No.
- Add Join Object if needed. Default value is Yes.
- Automatically add join conditions. Default value is Yes.
- Show adapter/application info in the graph. Default value is No.
- Automatically map all columns. Default value is No.
- Prior to load value (Relational). Default value is No changes.
- Prior to load value (Focus). Default value is No changes.
- Prior to load value (Flat File). Default value is No changes.
- Process Flow Preferences.
- Use application directory name with flow components. Default value is Yes.
- Add flows to run as stored procedures. Default value is No.
- Show Notes. Default value is No.
- Reporting Filter. You can select values for the following options:
- Database reads for a filter limit. You can enter a limit for initial database reads.
- Omit missing (null) values in Data Profiling charts. The default value is No.
- Target Defaults.
- Default ETL Target DBMS. You can select a configured adapter and connection for target tables in Upload, Quick Copy and Custom Copy.
- Enable SQL ETL Targets. Default value is Yes.
- Default ETL Target Application. Enter the name of the target application directory for target tables in Upload, Quick Copy and Custom Copy, or click the ellipsis (. . .) to select an application directory.
- Enable Bulk Load Targets. Default value is Yes.
- Show Load Options prompts. Default value is Yes.
Click Save when you have finished entering your preferences.
Displaying HOLD Keywords
You can display the keywords available for generating different types of HOLD files.
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- Click Settings on the ribbon, point to FOCUS
Sets and Info, and click HOLD Keywords.
The HOLD Keywords page opens, as shown in the following image.
- Select the following parameters.
- Optionally, select one or more Service Areas from
the Service Area drop-down list.
The areas are:
- Keywords specific to Relational DBMS formats.
- Keywords for Extended Bulk Load.
- Keywords specific to format DFIX.
- Keywords specific to format XML.
- Keywords specific to Excel formats.
- Keywords specific to stylesheet formats.
- Other format-specific keywords.
- Keywords to specify output for the data.
- Miscellaneous keywords.
- Obsolete keywords.
- Optionally, enter a keyword or keyword pattern in the Keyword text box.
- Optionally, enter a description or description pattern in the Description Contains text box for the keywords you want to see.
- Click Next.
- Optionally, select one or more Service Areas from
the Service Area drop-down list.
The HOLD Keywords Report is displayed, as shown in the following image.

Displaying Focus Limits
You can display limits for WebFOCUS requests and components, as well as limits that have been removed.
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- From the Settings section of the ribbon, click FOCUS
Sets and Info, and click Focus Limits.
The Focus Limits page opens, as shown in the following image.
- Select the following parameters.
- Optionally, select one or more service areas from the Service Area drop-down list.
You can select from the following service areas:
- Limits specific to Master Files.
- Limits specific to TABLE.
- Limits specific to JOIN and COMBINE.
- Limits specific to I/O.
- Limits specific to MODIFY.
- Limits specific to CREATE SYNONYM.
- Miscellaneous limits.
- Removed limits.
- Optionally, enter a limit name or pattern in the Limit text box.
- Optionally, enter a description or description pattern in the Description Contains text box.
- Click Next.
- Optionally, select one or more service areas from the Service Area drop-down list.
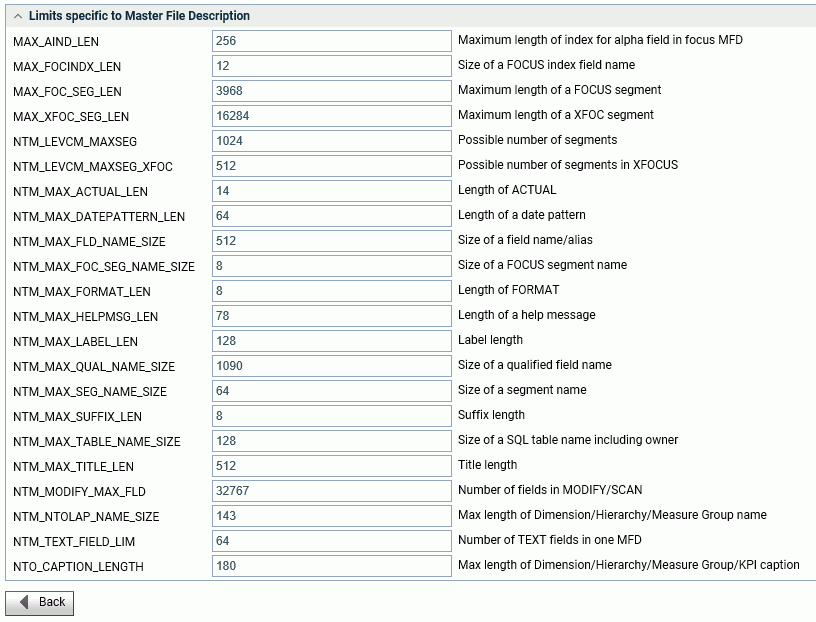
The FOCUS Limits Description report displays, as shown in the following image.
Displaying Error Messages
You can display all or different categories of error messages.
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- Click Settings on the ribbon, point to FOCUS
Sets and Info, and click Error Message Report.
The Filter Error Message Report page opens, as shown in the following image.
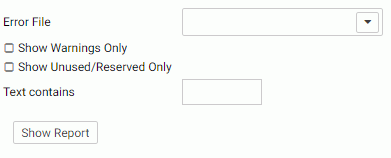
- Select the following parameters.
- Optionally, select one or more error files from the Error File drop-down list. Each error file on the list shows the range of error numbers contained in the file.
- Optionally, check the Show Warnings Only check box to limit the report to warning messages.
- Optionally, check the Show Unused/Reserved Only check box to control whether only unused or reserved messages display in the report.
- Optionally, enter text in the Text Contains text box for the messages you want to see.
- Click Show Report.
The Error Message report displays in a new tab, as shown in the following image.

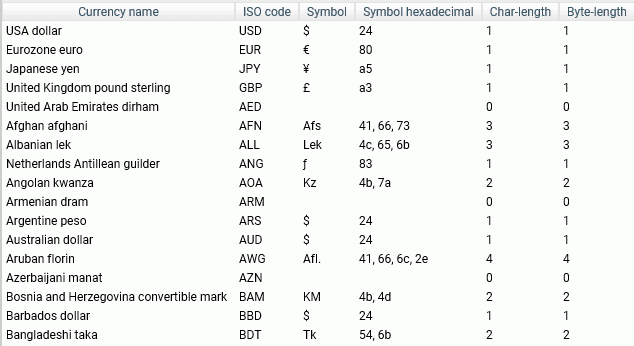
Displaying the Currency Report
The currency report lists currency names, ISO codes, currency symbols, currency symbols hexadecimal values, currency symbol character lengths, and currency symbol byte lengths.
To display the Currency Report, click Workspace on the sidebar, click Settings on the ribbon, point to FOCUS Sets and Info, and click Currency Report. The Currency Report page opens, as shown in the following image.
Determining Function Parameters
You can determine the parameters for a particular function from the Function Parameters Report. The report also includes a brief description of the function.
To display the Function Parameters Report:
- Click Workspace on the sidebar.
- Click Settings on the ribbon, point to FOCUS
Sets and Info, and click Function Parameters Report.
The IBI Functions Report page opens, as shown in the following image.
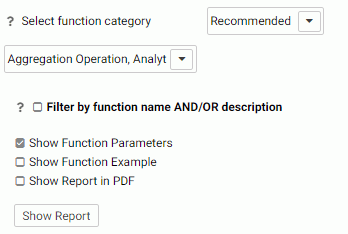
- Select the following parameters.
- Optionally, select one or more function categories from the Function Category drop-down list. The choices are Recommended, Legacy, and All.
- All of the functions in the category you chose are selected by default. Optionally, deselect one or more function types from the drop-down list, if you do not want to see those function types.
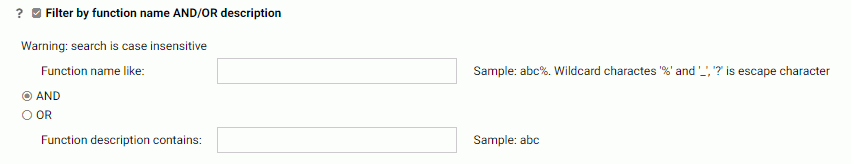
- Optionally, click Filter by function name AND/OR description to
provide a name or pattern for the function names and/or descriptions you want
to see. as shown in the following image.
- Optionally, click Show Function Example to see an example of using the function.
- Optionally, click Show Report in PDF to generate a PDF version of the report.
- Click Show Report.
The Function Parameters Report is displayed, as shown in the following image.
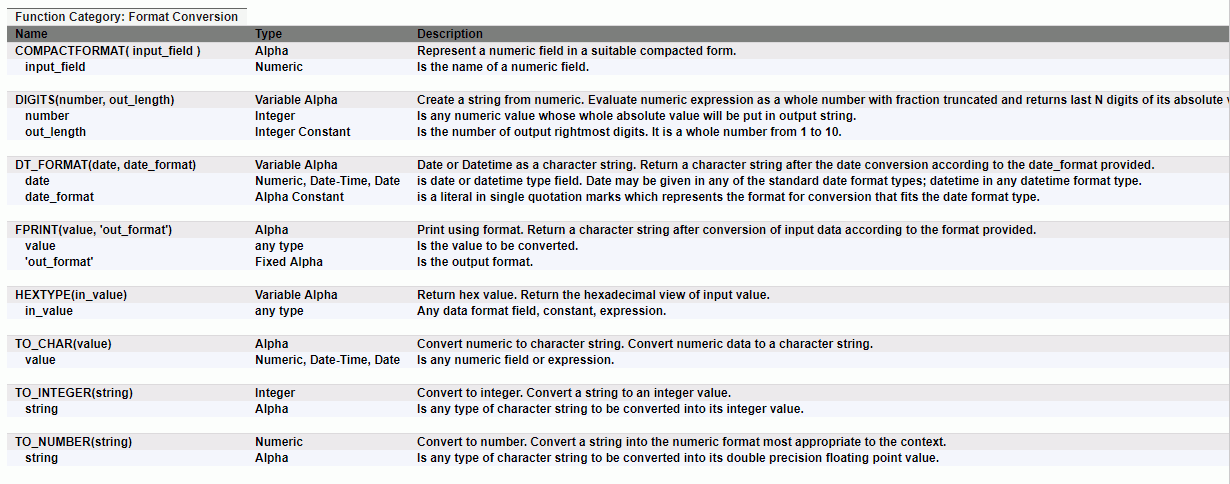
Configuring Geographic Information
|
Topics: |
|
How to: |
Geographic roles have been unified to access 58 world administrative boundaries down to the postal code level, out of the box. You can access administrative boundaries for approximately 250 countries with a second level license, which is a paid service from Esri. Enter your second level license code by clicking the License button on the ribbon.
The server has a geographic configuration editor for customizing the list of geographic roles, basemaps, reference layers, and demographic layers. A customized geographic role can reference either an uploaded shapefile or an existing Esri Feature Layer.
Note:
- You must configure the Adapter for ESRI ArcGIS in order to use many of the geographic features. For more information on configuring the adapter, see the Adapter Administration manual.
- The server must be configured for Unicode.
- To view the list of first and second level administrative boundaries, click General maps info on the Geo Services menu. The rows that have the value Paid in the Maps license column describe administrative boundaries available with a second level license. Right-click a column to see information about the data for that geographic role.
Procedure: How to Edit Geographic Configuration Settings
By default, the server is configured for unified geographic roles. This configuration is controlled by the following settings.
- Navigate to the Workspace page, click Settings, point to Geo Services, and click Edit settings.
The Change Settings for GEO services page opens, as shown in the following image.
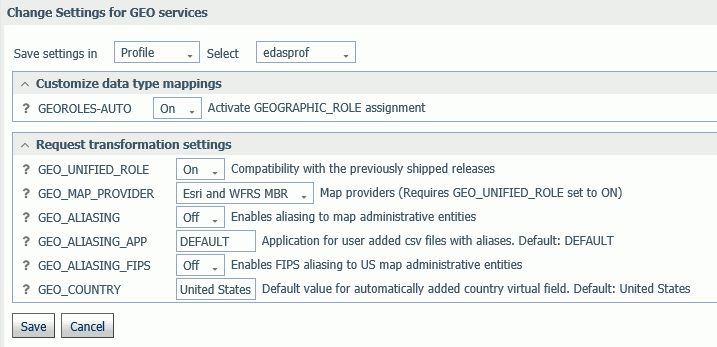
- The following setting controls whether geographic role assignments are automatically assigned using field name analysis.
GEOROLES-AUTO. The default value is On. For example, if an alphanumeric field has the name COUNTRY, it will be assigned the geographic role Country.
- The following settings control unified geographic roles.
- GEO_UNIFIED_ROLE. This compatibility setting must be turned on (the default) to activate unified geographic roles. Turn it off to use geographic roles from prior releases. On indicates that the new shorter set of geographic roles that combines subsets of previously used roles will be used. Off will use geographic roles from previously shipped releases.
- GEO_MAP_PROVIDER. Assigns names of the providers of geographic maps. The list of names should be separated with slashes to be used by transformation code for mapping. Default is ALL. The currently supported set of providers includes WFRS (geographic boundaries distributed in the Reporting Server) and ESRI.
- GEO_ALIASING. On enables aliasing to map administrative entities. Aliasing is a mechanism to support alternative names/spellings to the administrative names used as keys to find the corresponding geometry. Caution, incorrect results will be reported on a map in the case where the column data contains variations of names/spellings for the same administrative entity (resolved to the same key). Alias names are stored in .csv files. Shipped aliasing files are located in the geomaps sub-directory of the etc folder under EDAHOME. The naming convention is geo_srv_dbl_geo_role. Each data file has an associated synonym with the same name. Aliasing is currently supported for the four geo roles COUNTRY, STATE, COUNTY, and CITY. The STATE aliasing data file includes the valid country name for each state. COUNTY and CITY files include valid country and state names. Valid means the actual key value used to fetch a geometry The default value is off.
-
GEO_ALIASING_APP. Sets an application name for user-added .csv files with aliases. DEFAULT means no user files. User-added alias data files
are supported for the four geo roles COUNTRY, STATE, COUNTY, and CITY (see the description for the GEO_ALIASING setting).
The default value is DEFAULT, which uses the server aliasing files.
The best practice is to copy the desired. csv file from the _edahome/etc/geomaps folder to the application folder named in this setting, and edit it, changing aliases or adding records with new ones. There are four focexecs named geo_srv_mapkey_<geo_role> that have mandatory parameter ISO2 country name. The following is a request example that reports city names for South Africa sorted by state/province name.
EX geo_srv_mapkey_city ISO2='ZA'
Following is an example of user-created records (based on the obtained report):
"South Africa", "Gauteng", "Johannesburg", "City of Johannesburg" "South Africa", "Western Cape", "Paarl", "Drakenstein"
- GEO_ALIASING_FIPS. On enables FIPS aliasing to US map administrative entities. This setting requires GEO_ALIASING to be on. The data file with the United State FIPS aliases is processed as an extension to the main aliases data file The default value is off.
- GEO_COUNTRY. Assigns a default value for an automatically added DEFINE field with GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE 'Country'. This mechanism is in effect during the create metadata process when the setting GEOROLES-AUTO is ON and a column with geo role COUNTRY is not detected. The generated DEFINE field will be used to create geo hierarchies required in mapping. The default value is 'United States'.
- GEOROLE_2_MBRLEVEL. CUSTOM enables customized per country mapping of the geo roles (STATE, COUNTY, and CITY) to the MBR administrative levels. STANDARD sets uniform mapping of geo roles (STATE, COUNTY, and CITY) for all countries to the MBR administrative levels (1, 3, and 5 respectively). There is a geo_role2mbrlev focexec to list countries with customized admin levels. The report does not depend on this setting.
- Click Save.
Editing the Geographic Configuration
|
Reference: |
The GEO configuration editor provides a tool for editing or adding properties for geographic roles, basemaps, reference layers, and demographic layers. In addition, it enables you to add maps and shapefiles to the configuration.
Click Workspace on the sidebar. Click Settings, point to Geo Services, then click Edit Configuration. The GEO configuration editor opens displaying the configured geographic roles, as shown in the following image.
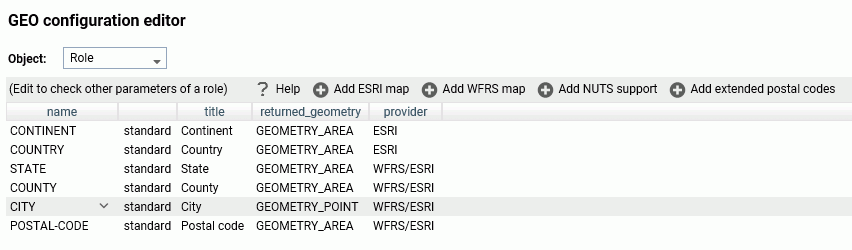
You can select the following objects from the Object drop-down list.
- Role.
- Basemap.
- ContextLayer.
You can edit the properties for a basemap or context layer (reference layer or demographic layer), or add a new one. You cannot edit the properties of a standard geographic role. To add a customized geographic role, you first add an Esri map or a shapefile (WFRS map) and assign the geographic role to the map or shapefile.
Reference: Editing the List of Geographic Roles
The following standard unified geographic roles are configured by default and cannot be changed. These geographic roles create a hierarchy that can be used to drill down or up between levels of administration in maps, reports, or charts.
- CONTINENT.
- COUNTRY.
- STATE.
- COUNTY.
- CITY.
- POSTAL CODE.
To add a geographic role to the configuration, you can add a new Esri map or a shapefile hosted by the Server and associate a geographic role with the new map. You can also implement NUTS geographic roles support.
Configuring Properties of Geographic Roles
The following describes columns for geographic roles in the configuration editor.
- name
-
Is the unique name of the geographic role. It cannot have spaces, but it can have underscores (_).
Next to the name is an indicator of whether the role is a standard role or a customized role.
- title
-
Is the description of the geographic role that is displayed in reports and in drop-down lists in the WebFOCUS tools.
- returned_geometry
-
Is the type of geographic data returned from the map service for rendering on the map.
Valid values include:
- GEOMETRY_AREA
- GEOMETRY_POINT
- GEOMETRY_LINE
When you have configured the properties, click OK to return to the Geo Configuration Editor.
The new role will display on the list of roles, Click Save to save it in the geographic configuration.
Adding a New Role for an Esri Map
To add an Esri geographic role, click Add ESRI map on the Geographic Configuration Editor.
The Create a new ESRI map role dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
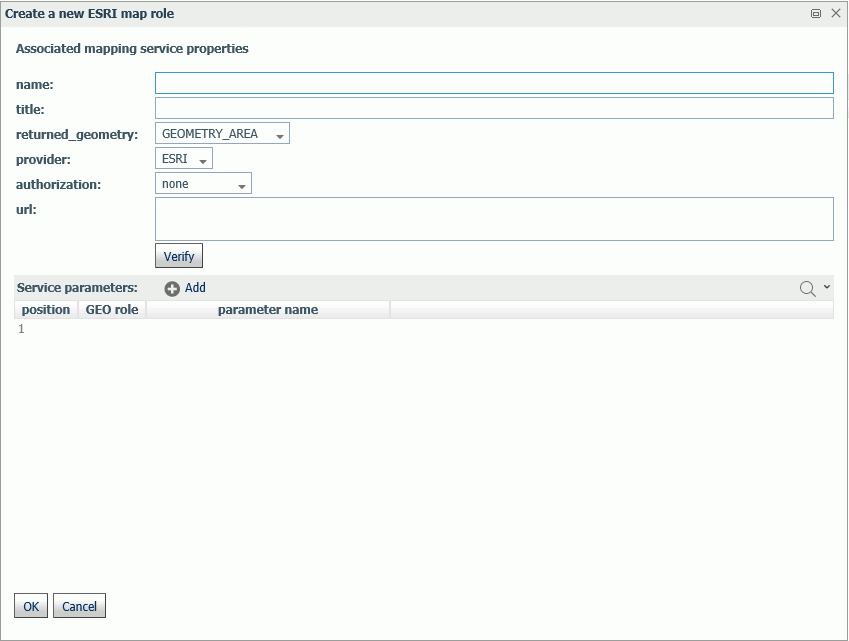
Configure the following map service properties.
- name
-
Is a name for the geographic role.
- title
-
Is a title to display in the WebFOCUS tools.
- returned_geography
-
Select the type of geometry that is returned from the map service for this role. Valid values are:
- GEOMETRY_AREA. Returns JSON polygon definitions.
- GEOMETRY_LINE. Returns JSON line definitions.
- GEOMETRY_POINT. Returns a JSON point.
- url
-
Is the URL to the map service that provides the geographic data.
Click Verify after entering the URL to verify that the map service is available by going to the specified URL.
- Service Parameters
-
Add as parameters any additional geographic roles needed to identify the exact location of the new role. For example, a city name needs state and country parameters.
Example: Adding the WebFOCUS Regions Geographic Role
The following properties add the WebFOCUS Regions role to the configuration.
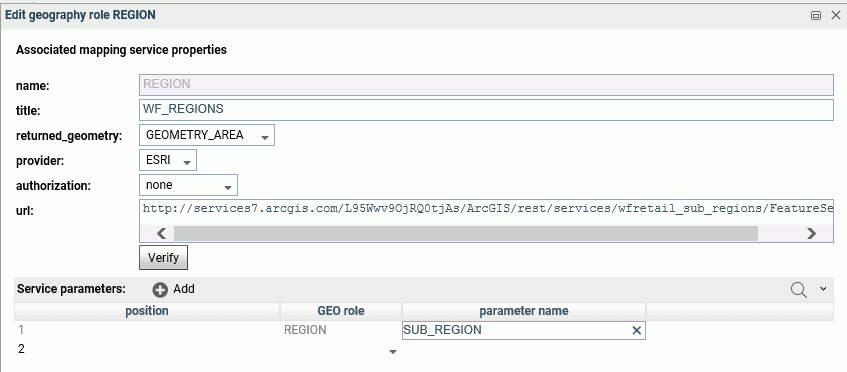
Note: The parameter name corresponds to the field name in the FeatureLayer referenced in the following URL:
http://services7.arcgis.com/L95Wwv9OjRQ0tjAs/ArcGIS/rest/services/wfretail_sub_regions/FeatureServer/0
Click OK when you have finished configuring the properties.
The new role is added to the configuration as a customized role, as shown in the following image.
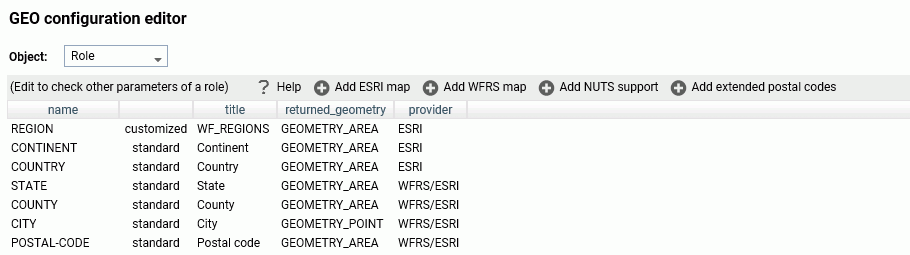
Click Save to save this role to the configuration.
The following request uses the WebFOCUS Regions geographic role in a map request.
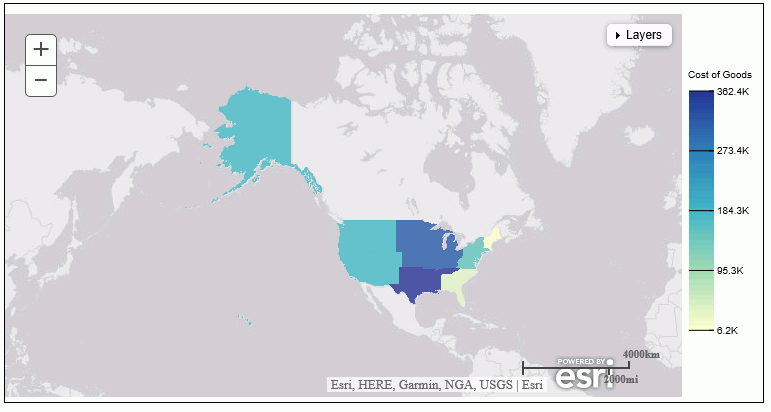
DEFINE FILE WF_RETAIL_LITE REGION/A50 (GEOGRAPHIC_ROLE=REGION) = BUSINESS_SUB_REGION; END GRAPH FILE WF_RETAIL_LITE SUM COGS_US BY REGION WHERE COUNTRY_NAME EQ 'United States' ON GRAPH PCHOLD FORMAT JSCHART ON GRAPH SET LOOKGRAPH CHOROPLETH ON GRAPH SET STYLE * TYPE=REPORT, CHART-LOOK=com.esri.map, $ TYPE=DATA, COLUMN=N2, BUCKET=color, $ *GRAPH_JS_FINAL "extensions": { "com.esri.map": { "overlayLayers": [ { "ibiDataLayer": { "map-metadata": { "map_by_field": " REGION" } } } ], "baseMapInfo": { "customBaseMaps": [ { "ibiBaseLayer": "gray" } ] } } } *END ENDSTYLE END
The output is shown in the following image.
Adding a New Role for a Server-Hosted Map
A server-hosted map is based on a shapefile. You must upload the shapefile (.dbf) to an application folder accessible to the server. The server will transform it to ibijson format.
An ESRI shape file is actually a collection of at least four files:
- .dbf file. The .dbf file is a standard database file used to store attribute data and object IDs. A .dbf file is mandatory for shape files.
- .shp file. The .shp file is a mandatory Esri file that gives features their geometry. Every shapefile has its own .shp file that represents spatial vector data.
- .shx file. The .shx file is a mandatory Esri shape index position file. This type of file is used to search forward and backwards.
- .prj file. The .prj file is an optional file that contains the metadata associated with the shapefiles coordinate and projection system.
All files must have exactly the same name and to be located in the same directory. If they are not, the shapefile conversion will fail.
When there are several possible keys associated with a geometry, a drop down list of detected key names will be displayed. Select any one of these fields. No selection required when there is a single geometry key.
The shapefile should only be in the GCS_WGS_1984 - World Geodetic System 1984 (decimal degrees) coordinate system.
To add a geographic role for a Server-hosted map, click Add WFRS map on the Geographic Configuration Editor.
The Add WFRS hosted map dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
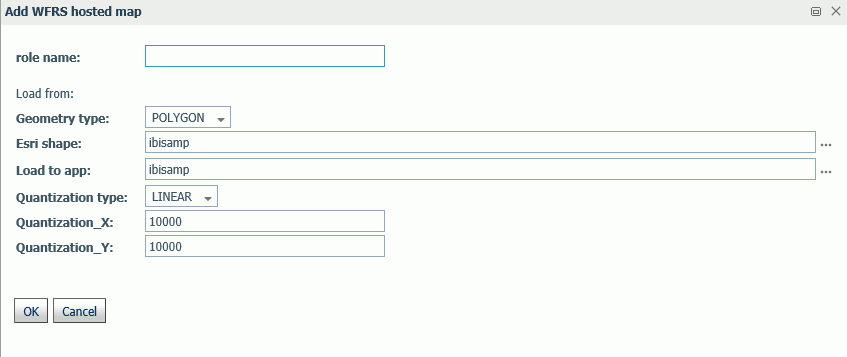
Configure the following properties.
- role name
-
Is a name for the geographic role.
- Geometry type
-
Select either POLYGON or POINT from the drop-down list.
- Esri shape
-
Enter the name of the application directory where the shapefile resides, or click the ellipsis (...) to navigate to the application directory. Then select the .dbf file for the role.
- Load to app
-
Enter the name of the application directory where you want to place the ibijson file, or click the ellipsis (...) to navigate to the application directory.
- Quantization type
-
Quantization is the process of transforming a large set of input values to a smaller set of values. When transforming the shapefile, the server will quantize points that are too close together in order to optimize map rendering performance. Two methods are available for quantization, LINEAR or GRID. The default is LINEAR.
- Quantization_X
-
Is the threshold value for the x-axis.
- Quantization_Y
-
Is the threshold value for the y-axis.
If the map has multiple keys, a drop-down list displays so that you can select one.
Click OK when you have finished configuring the properties.
The new role is added to the configuration as a customized role, as shown in the following image.
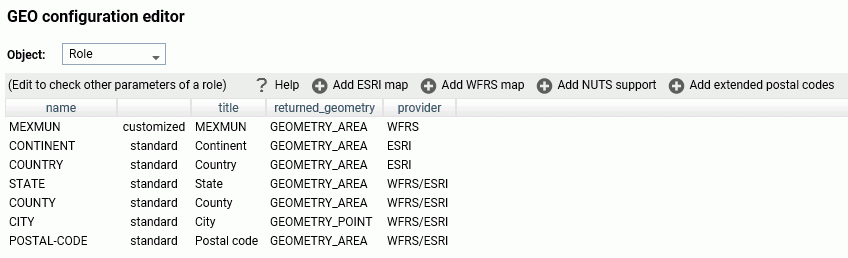
Click Save to save this role to the configuration.
You can test the role by right-clicking the role in the configuration editor and clicking Test. A sample map will be generated, as shown in the following image.
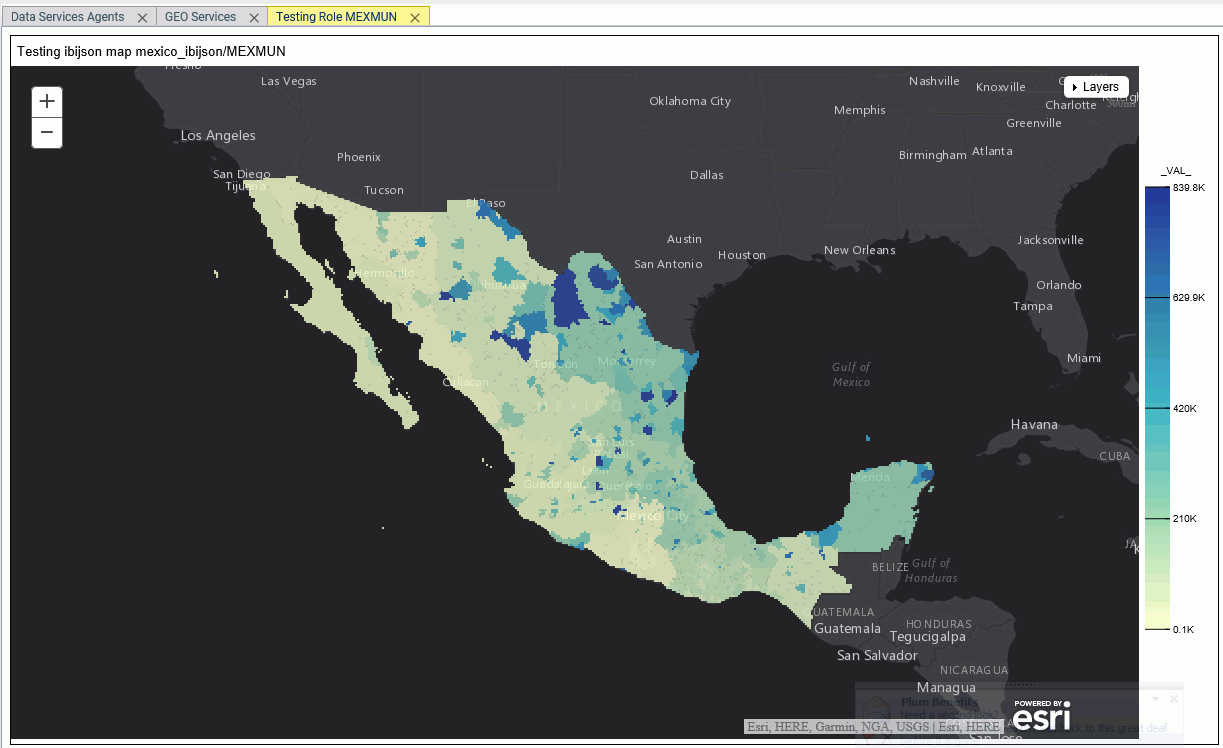
Adding NUTS Support
Nomenclature of territorial units for statistics (NUTS) are geographic roles specific to the European Union.
To add NUTS geographic roles to the configuration, click Add NUTS support on the Geographic Configuration Editor.
The NUTS geographic roles are added, as shown in the following image.
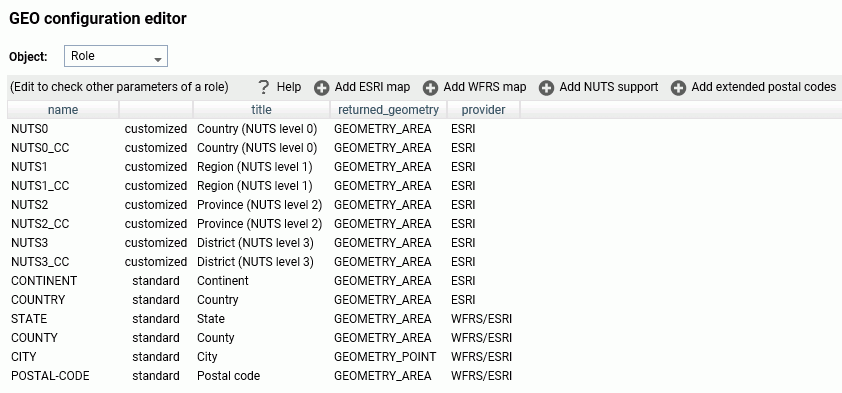
Click Save to save these roles to the configuration.
Adding Support for Extended Postal Codes
Click Add extended postal codes to add support for Level 1 and Level 2 postal codes used in certain countries.
Customizing Vocabulary Rules
For each geographic role, a set of vocabulary rules define how to recognize when a field name should automatically be assigned to that role. If you right-click a role, you can click Customize vocabulary from the shortcut menu.
Elements in a rule are connected by the Boolean logic operation OR (only one needs to be satisfied). Each vocabulary element contains words enclosed with special characters. Words in the rule element are connected by the Boolean logic operation AND (all need to be satisfied).
A word may be prefixed and/or suffixed with the percent character (%), which is a placeholder for any sequence of characters. If an element contains more than one word, each word has to be prefixed by the character plus (+) or minus (-). Plus indicates that the word must be found in the column name. Minus indicates that word must not be found in the column name.
For example, the following are the vocabulary rules for the role COUNTRY.
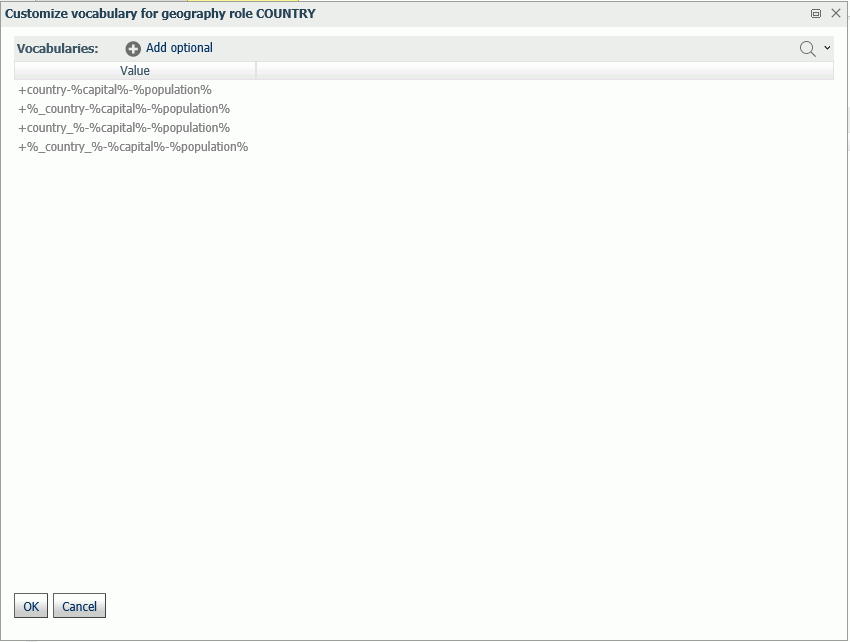
To add another rule, click Add optional.
When you are finished, click OK.
Click Save to save these rules to the configuration.
Reference: Customizing the List of Basemaps
You can edit an existing basemap definition or add a custom basemap.
Basemaps that are not vector maps are pre-rendered image tiles. Vector basemaps are delivered from ArcGIS Online as vector tiles that are rendered on the client based on a style file that is delivered with the vector tiles. This provides customization options not available with pre-rendered image tiles.
A default set of vector basemaps is configured in the GEO configuration editor in the Server. However, you can configure additional vector basemaps as needed. You can find the basemap URLs and Style URLs at http://www.arcgis.com.
Using Standard Basemaps
To add a new basemap or customize an existing basemap, select Basemap from the Object drop-down list.
The following image shows the GEO configuration editor with the Basemap object selected, showing the list of standard basemaps.
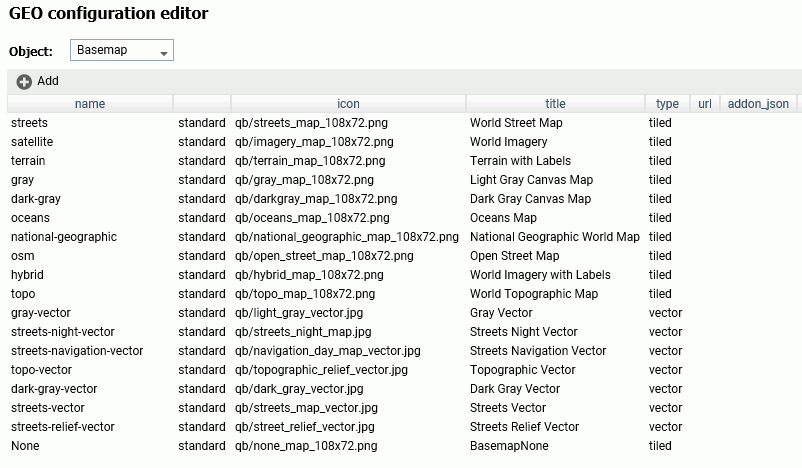
Configuring Basemap Properties
The following is a description of the properties used for basemap configuration.
- name
-
Is the name of the basemap.
Next to the name is an indicator of whether the basemap is a standard basemap or a customized basemap.
- icon
-
Is the name of the thumbnail for the basemap (for a standard basemap) or the URL to the thumbnail (for a customized basemap) that will appear on the Basemap drop-down list in the WebFOCUS tools or the Change Basemap map widget.
- title
-
Is a title to display on the Basemap drop-down list in the WebFOCUS tools or the Change Basemap map widget.
- url
-
Is the URL to the map service that provides the basemap, for a customized basemap. The map service URL can be copied from the URL field on the page showing a custom basemap. For a standard basemap, the URL is already stored in the server geographic configuration file and is not displayed.
- type
-
Valid values are tiled and vector.
- addon_json
-
Specifies additional JSON properties for rendering the map. For a custom vector basemap, enter the basemap map service URLs and Style URLs needed for rendering the map. The map can consist of an array of layers, each with a URL and its style URL. The style URL for each layer can be found by clicking View Style on the page showing the map layer. The map service URL for each layer can be copied from the URL field on the page showing the map layer. Enter the information in the following format.
{"baseMapLayers": [ {"url": "url_to_map_service", "styleUrl": "url_to_style"}, {"url": "url_to_map_service", "styleUrl": "url_to_style"}, ... ] }Note: If the vector basemap has multiple layers, its page on ArcGIS online will have links to each layer.
Editing the Properties of a Standard Basemap
To customize the properties of an existing basemap, right-click the basemap line and click Customize BASEMAP.
The Customize Basemap dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
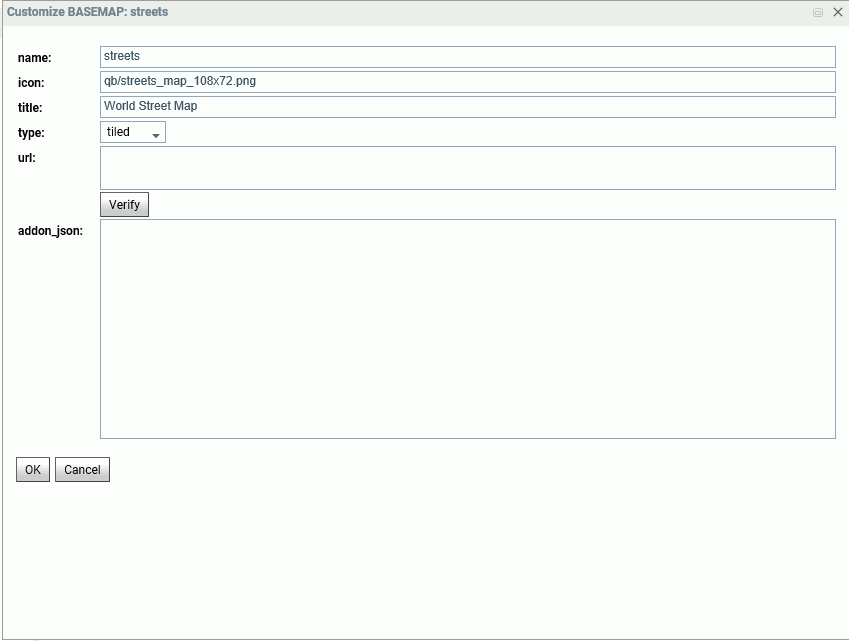
Edit the properties you want to change. If you change the URL, you can click Verify to make sure the map service is valid and accessible.
When you are finished, click OK, then click Save on the GEO configuration editor Basemaps page.
Adding a Custom Basemap
To add a new basemap to the configuration, click Add.
The Create a BASEMAP dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
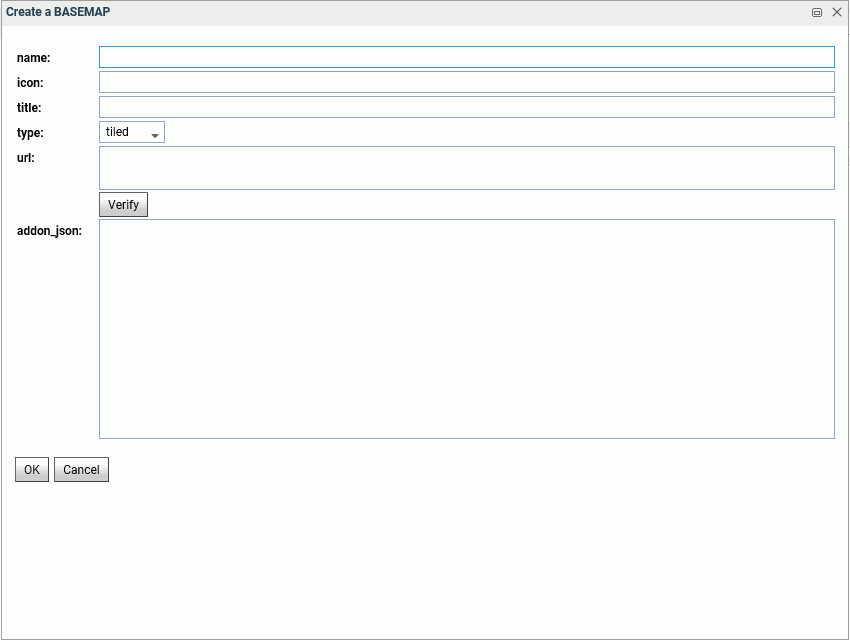
Enter a name for the basemap, a URL to the thumbnail, a title to display, and the URL to the map service that provides the basemap, and click Verify.
When you have configured the properties, click OK, then click Save on the GEO configuration editor Basemap page.
Example: Configuring the Nova Vector Basemap
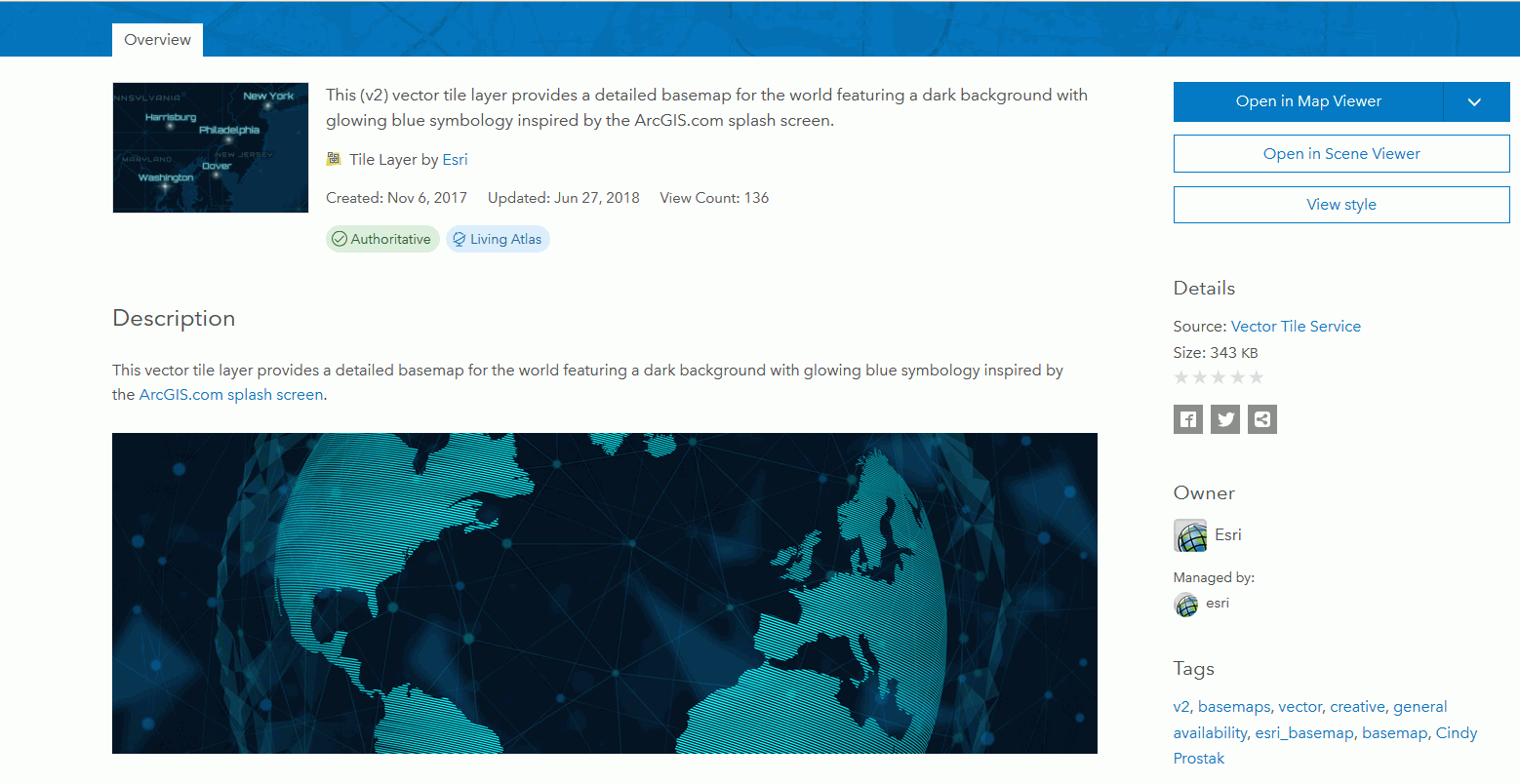
The following steps are needed to determine the properties associated with the Nova vector basemap.
- Navigate to the following URL for the Nova basemap.
https://www.arcgis.com/home/item.html?id=75f4dfdff19e445395653121a95a85db.
The Nova basemap page is shown in the following image.
In the addon_json syntax, you need the styleUrl for each basemap URL defined in the vector basemap.
- Click the View Style button to retrieve the styleUrl. In this case, it is the following URL.
- Add the following URL for the Esri vector map service in both the url field in the GEO configuration editor and in the addon_json
syntax for this basemap. You can copy this location from the URL field on the lower right of the Nova basemap page.
https://basemaps.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/World_Basemap_v2/VectorTileServer
- The icon value must be a URL reference. This example uses the one referenced in the thumbnail of the webmap, which is the following URL (retrieved by right-clicking the thumbnail image at the top of the page and copying the image location).
Add these properties in the GEO configuration editor to define the Nova vector basemap, which consists of a single layer. Add the name, type, and a title, as follows.
name: Nova
title: Nova
url: https://basemaps.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/World_Basemap_v2/VectorTileServer
addon_json:
{"baseMapLayers":
[
{"url": "https://basemaps.arcgis.com/arcgis/rest/services/World_Basemap_v2/VectorTileServer",
"styleUrl": "http://www.arcgis.com/sharing/rest/content/items/75f4dfdff19e445395653121a95a85db/resources/styles/root.json"
}
]
}The following image shows the Create a BASEMAP page for configuring the Nova vector basemap in the Reporting Server GEO configuration editor.
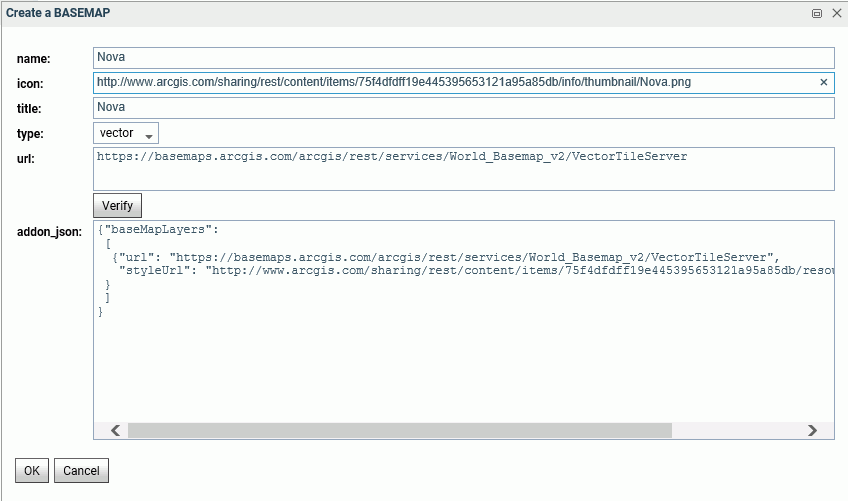
After clicking OK, then Save, the custom vector basemap becomes available for selection in the App Studio Properties panel for the Esri map component, as shown in the following image.
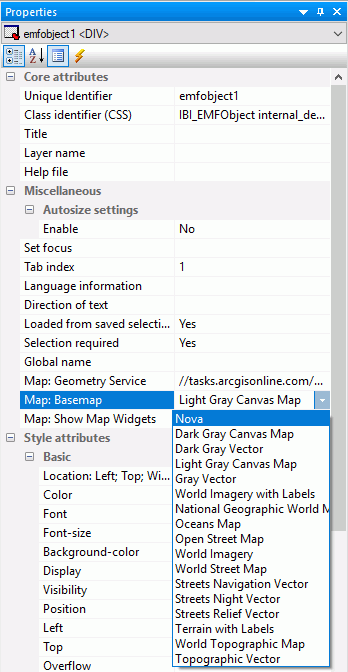
The App Studio Esri component in this example uses the following request, named customer_locations.fex.
TABLE FILE WF_RETAIL_LITE
PRINT
ID_CUSTOMER
COGS_US
QUANTITY_SOLD
COMPUTE LONGITUDE/D12.2 =CUSTOMER_LONGITUDE;
COMPUTE LATITUDE/D12.2 = CUSTOMER_LATITUDE;
BY STATE_PROV_NAME
BY ID_CUSTOMER NOPRINT
WHERE COUNTRY_NAME EQ 'United States';
ON TABLE NOTOTAL
ON TABLE PCHOLD FORMAT XML
ENDConfigure the Settings panel for the Esri map to use this request for a Point of Interest layer.
Running the HTML page generates the following map, with the Nova vector basemap as the base layer.
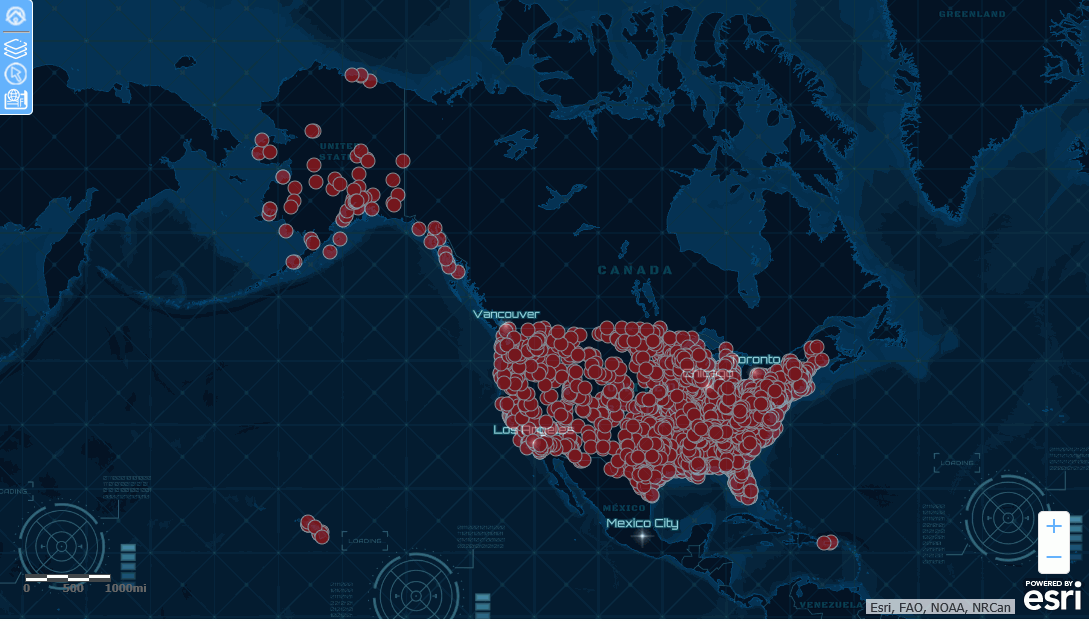
The Nova vector basemap is also available in the Change Basemap widget, as shown in the following image.
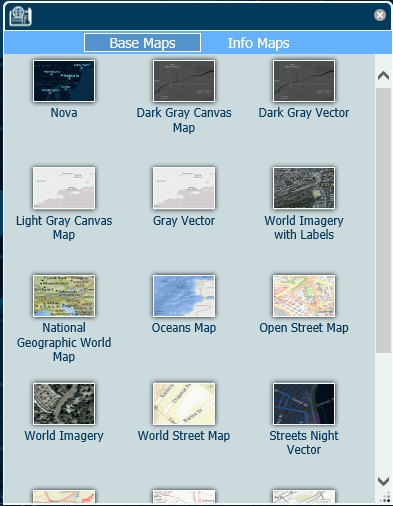
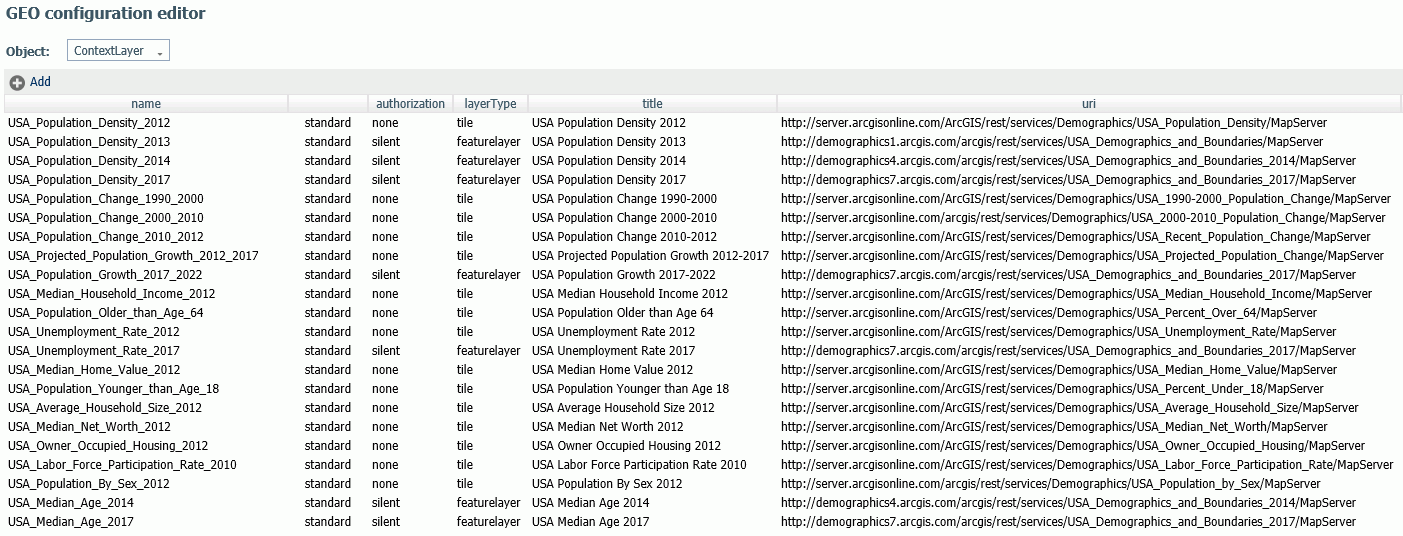
Reference: Customizing the List of Context Layers
To add a new context layer or customize an existing context layer, select ContextLayer from the Object drop-down list.
The following image shows the GEO configuration editor with the ContextLayer object selected.
Configuring Context Layer Properties
Following is a description of the properties used for context layer configuration.
- name
-
Is the name of the context layer.
Next to the name is an indicator of whether the context layer is a standard context layer or a customized context layer.
- authorization
-
Is the type of authentication needed to access this context layer. Valid values are:
-
silent. Credentials for your ArcGIS application are provided in the connection string of the Adapter for Esri ArcGIS.
Note: For instructions for configuring the Adapter for Esri ArcGIS, see the Adapter Administration manual.
- none. No authorization is needed.
- named. User credentials are provided in the connection string of the Adapter for Esri.
- on premises. User credentials for a locally hosted ArcGIS server are provided in the connection string of the Adapter for Esri.
-
silent. Credentials for your ArcGIS application are provided in the connection string of the Adapter for Esri ArcGIS.
- layer type
-
Is the type of context layer. For a cached layer, the layer type is tile. For a layer that is rendered dynamically, the layer type is featurelayer.
- title
-
Is a title to display on the demographic layer drop-down list in the WebFOCUS tools.
- uri
-
Is the URL to the map service that provides the context layer.
- addon_json
-
Specifies additional JSON properties needed for rendering the context layer. For example, smartMapping properties define the border styles within the context layer.
Customizing the Properties of an Existing Context Layer
To customize the properties of an existing context layer, click the down arrow next to a context layer name or right-click the context layer line and click Customize context layer.
The Customize CONTEXTLAYER dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
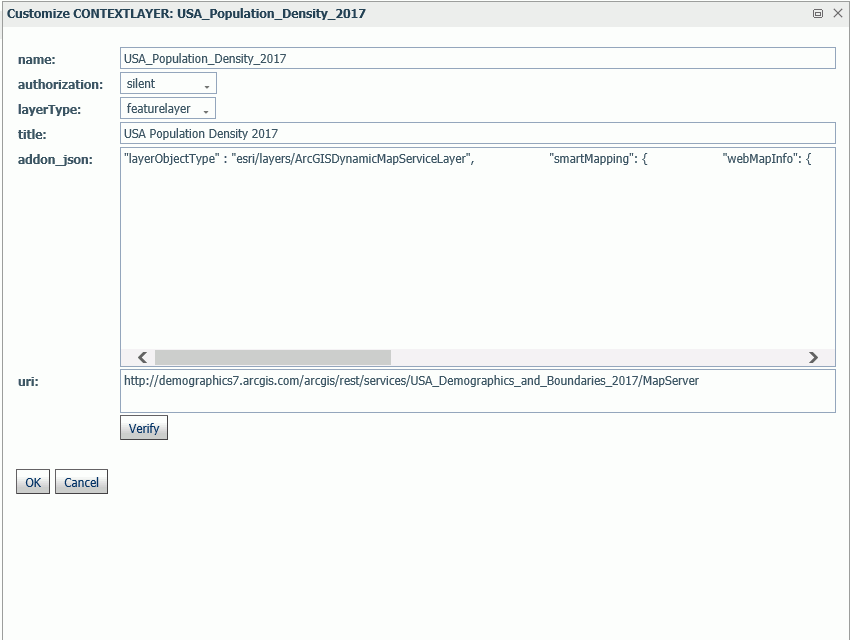
Edit the properties you want to change. If you change the URI, you can click Verify to make sure the map service is valid and accessible.
When you are finished, click OK, then click Save on the GEO configuration editor Context Layers page.
Adding a New Context Layer
To add a new context layer to the configuration, click Add.
The Create a Customized CONTEXTLAYER dialog box opens, as shown in the following image.
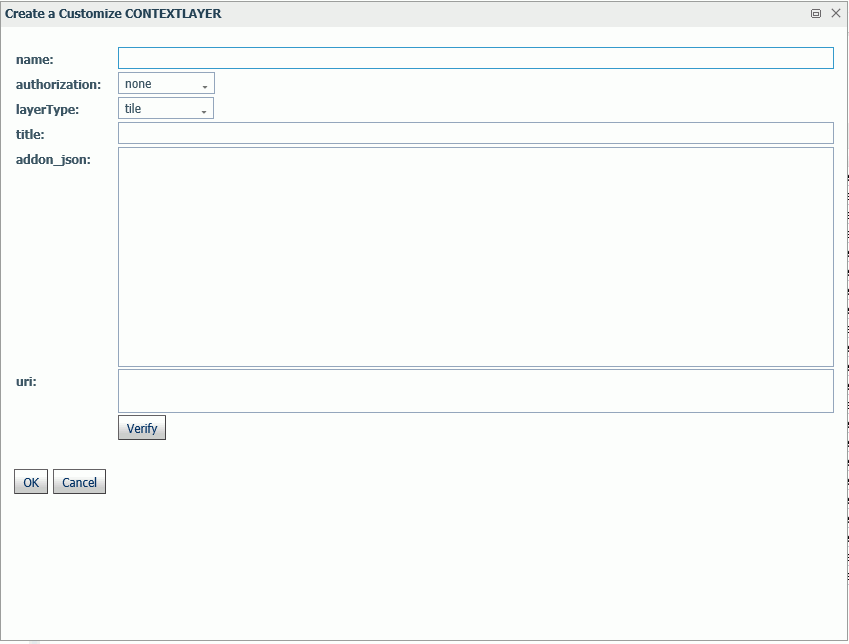
Enter a name for the context layer, the authorization type, a layer type, a title to display, any additional JSON needed for rendering the context layer, and the URI to the map service that provides the context layer, and click Verify.
When you have configured the properties, click OK, then click Save on the GEO configuration editor Context Layer page.
License Settings
You can view and change the current license code and provide and/or change your site code using the License Management page.
The license code is encoded to determine the configuration, additional products available in the configuration, the number of CPUs on the server, and the number of user seats the configuration supports.
For more information on how to obtain a new license code, contact Customer Support Services or your local Information Builders sales office.
To access these settings, click Workspace on the sidebar. From the ribbon, click License, then click License on the menu.
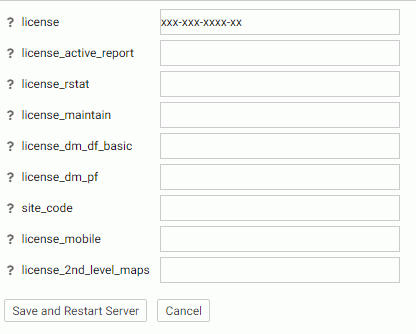
The following License Management settings are saved in the edaserv.cfg file:
When you have completed your entries, click Save and Restart Server.
- license
-
Enter the license number (required for the type of server you are using).
- license_active_report
-
Enter the license number for WebFOCUS Active Technologies.
- license_rstat
-
Enter the license number for the RStat scoring feature.
- license_maintain
-
Enter the license number for the Maintain Data feature.
- license_dm_df_basic
-
Enter the license number for the web DataMigrator data flow feature.
- license_dm_pf
-
Enter the license number for the web DataMigrator process flow feature.
- site_code
-
Enter the site code number (required for support calls).
- license_mobile
-
Enter the license number for the Mobile Faves feature.
- license_2nd_level_maps
-
Enter the license number for the second level maps feature.
Click Save and Restart Server.
Migrate Settings
The Migrate Settings page allows you to migrate a server from a previous release.
It is recommended that you migrate configuration information from previous releases after you verify the proper basic installation of the new release.
To migrate from a previous release:
- From the sidebar, click Workspace.
- From the
ribbon, click License, then click Migrate.
The Migrate page opens.
- Type the full path of the configuration instance directory (EDACONF) or click the ellipsis (...) and navigate to it.
- Click Continue.
| WebFOCUS | |
|
Feedback |