RScripts in RStat
|
Topics: |
An RScript can run plots, charts, summaries, model techniques, or even be used to execute scoring functionality using R. As of RStat 1.3.1, RScripts can run using RStat, and depending on the technique, the RScript, if used to create a scoring routine, can be converted to a C routine like a native RStat scoring technique. For both capabilities, the package referenced by the RScript needs to be loaded to the RStat environment in the R workspace. Without the R package, the script will not run. If the intent of the RScript is to create a model and output a C file for the scoring routine to be used by the WebFOCUS Reporting Server, then the feature requires a few naming conventions and a few other items to be existent.
Running an RScript
|
Topics: |
|
How to: |
To run the RScript, note the following:
- You need the package required by the RScript. This step is not covered in the manual.
- You need the RScript, which is run in the R environment by the WebFOCUS Reporting Server.
- R needs to be on the machine or configured with the WebFOCUS Reporting Server.
- Memory usage depends on the R architecture (32-bit or 64-bit) and the server memory. WebFOCUS will take the request and pass it on if the application is designed to do so. The WebFOCUS Server will take the output and present it in the format desired by the application.
Procedure: How to Run an RScript
- If starting a new process, in App Studio, on the Home tab, in the Modeling group, click Predictive Modeling to launch RStat. Otherwise, click the New button
on the RStat GUI.
- On the Data tab, in the Source area, select the RScript option.
- Click the
Filename list to browse for an RScript file.
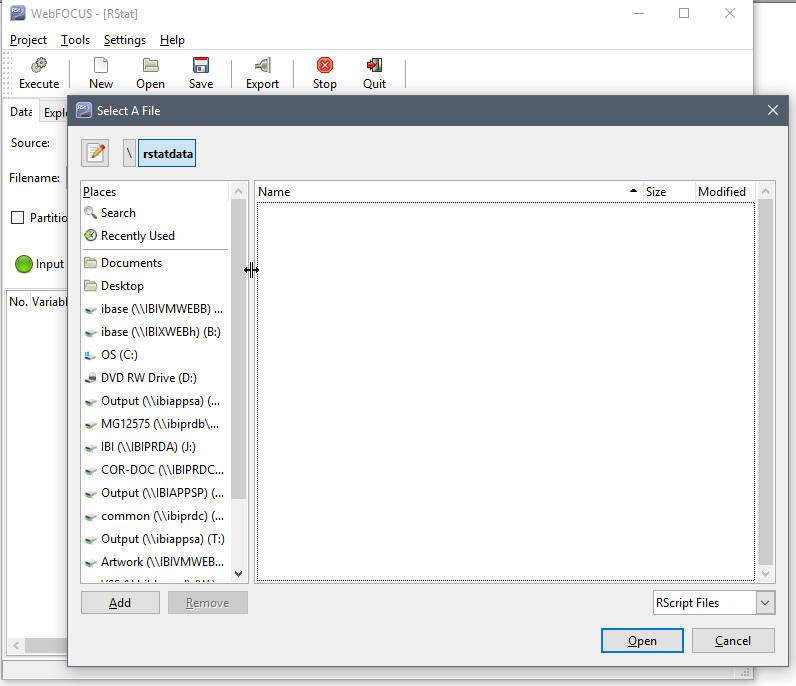
- If an RScript
file with an extension of .R or .r is loaded, click the Execute button.
The command in RScript will be loaded in R but no code will be shown
in the R GUI.
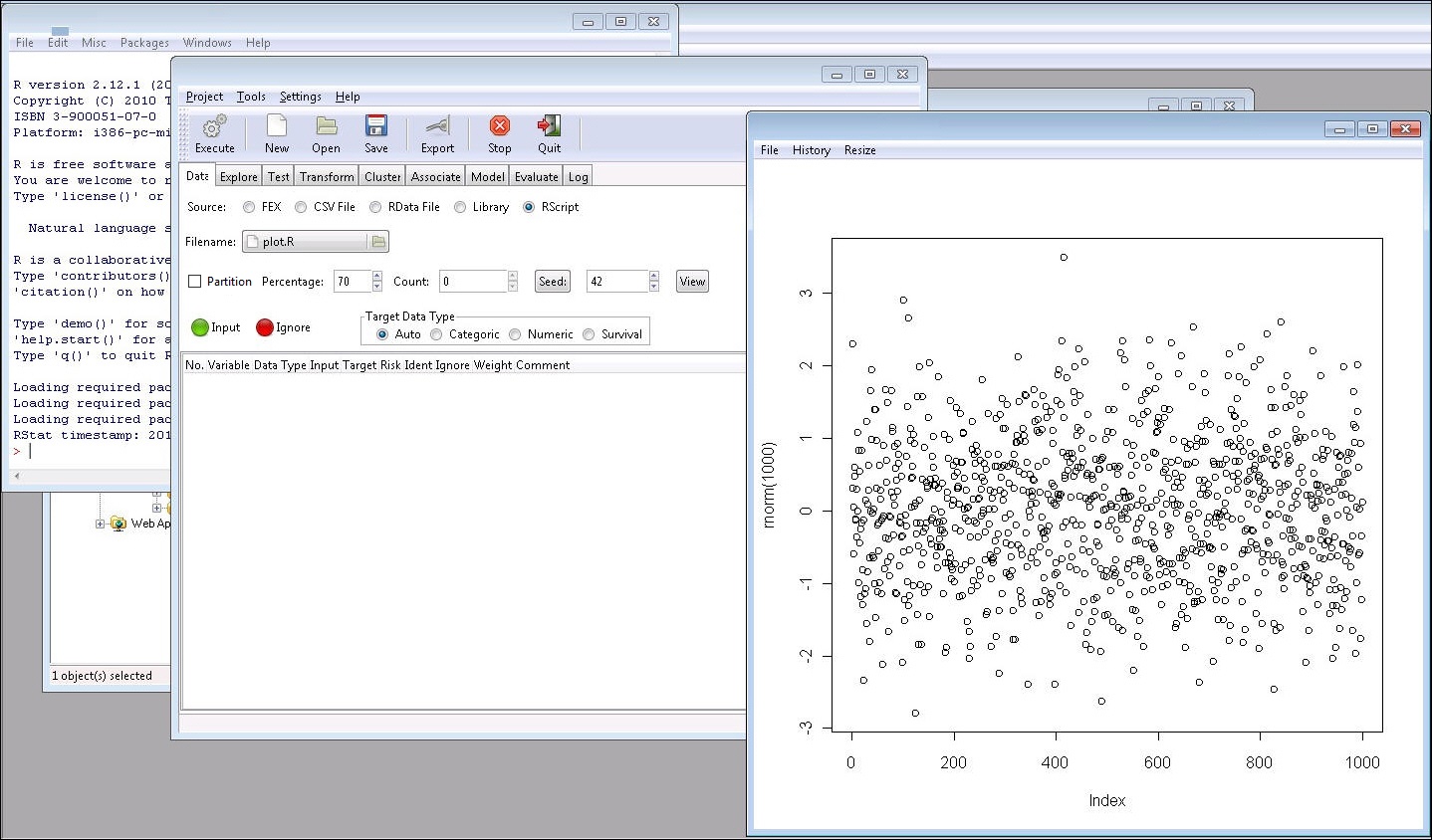
The following example shows an RScript that is executed to create a plot.
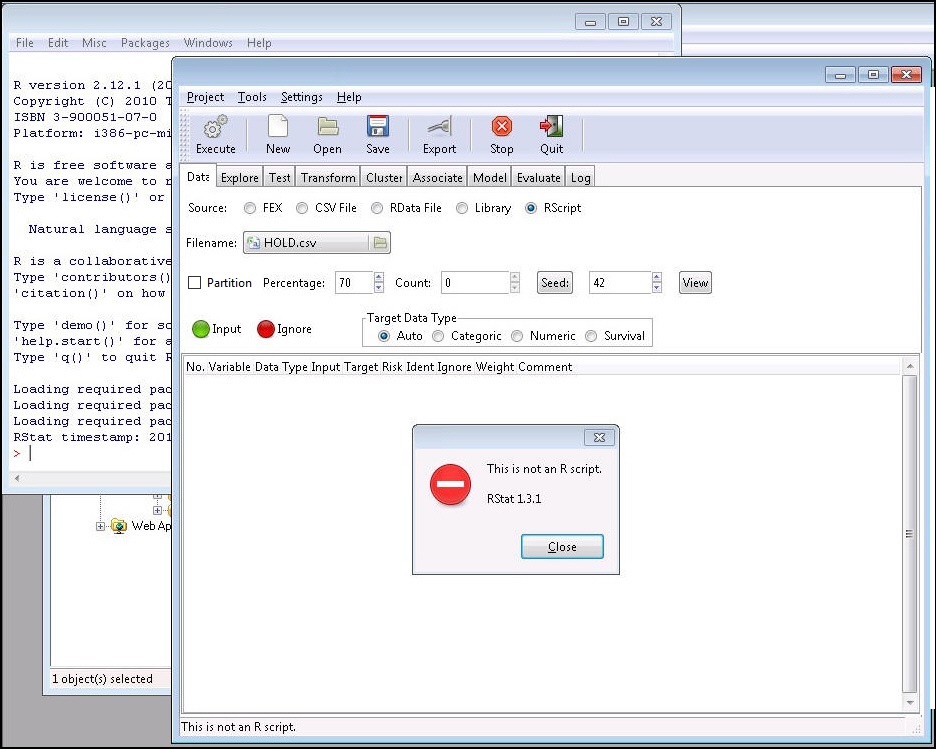
Note: Once the RScript button is active (selected), the user can upload an RScript. When a non-script file is selected (for example, a .csv file or a .txt file), a message appears, as shown in the following image. The error message will also be shown in the RStat status bar and log file. The RScript button is looking for a R code file with an extension of .R.
Running an RScript in Order to Create a C File
|
How to: |
|
Reference: |
To create the Scoring Routine C file from an RScript, note the following:
- You need the package required by the RScript. This step is not covered in the manual.
- You need the RScript, which is run in the R environment by the WebFOCUS Reporting Server.
- R needs to be on the machine or configured with the WebFOCUS Reporting Server.
- The scoring routine technique has to be a native to RStat. For example, Decision Tree, Regression, Survival, Neural Networks, and Clustering.
- The following variables
must be assigned:
- crs$dataset: the dataset used to build the model in the script.
- crs$rpart: model name defined in crs: glm for regression, rpart for decision trees, and hcluster for cluster.
- pmml.cmd: in the format: pmml.cmd <- "pmml(crs$rpart, dataset=crs$dataset)".
- Before clicking Export, you must first click the Model tab. Otherwise, it will export a .csv file since the RScript button resides on the Data tab. In addition, the file name needs to be assigned by the user.
Procedure: How to Run an RScript to Create C File Output
- If starting a new process, in App Studio, on the Home tab, in the Modeling group, click Predictive Modeling to launch RStat. Otherwise, click the New button
on the RStat GUI.

- On the Data tab, in the Source area, select the RScript option.
- Click the
Filename list to browse for an RScript file.

- If an RScript file with an extension of .R or .r is loaded, click the Execute button. The command in RScript will be loaded in R but no code will be shown in the R GUI.
- If you want
to export the model built in the RScript to a C routine, the following
variables must be assigned before exporting (take decision tree
as example):
- crs$dataset: the dataset used to build the model in the script.
- crs$rpart: model name defined in crs: glm for regression, rpart for decision trees, and hcluster for cluster.
- pmml.cmd: in the format: pmml.cmd <- "pmml(crs$rpart, dataset=crs$dataset)"
- Before clicking Export, you must first click the Model tab. Otherwise, the execute action will export a .csv file since the RScript button resides on the Data tab.
- Provide
the name for the C file to be created.
Reference: Usage Notes for RScript to Create Scoring Routines
If you choose not to load the data set in RStat but want to export a C routine, you can load an .RData file or use a saved pmml/XML file to export the C routine in the R console with RStat opened. RStat will check crs$dataset before exporting any file. Thus, non-data exporting only can be done in the R console with an RStat session opened.
The .RData file saves the model summary as an R workspace. The example below shows related codes for the decision tree.
decTree<-rpart(PRICE_1991~.,dataset) save( decTree, file = 'wine_training_rpart.rdata')
The two code lines above should be included in the user script.
The following code will be the script uploaded by the RScript button in RStat 1.4 and higher, which first loads the .RData file to pass the model summary to crs$rpart, and then further defines the 'pmml.cmd' command.
load('wine_training_rpart.rdata')
crs$rpart<-decTree
pmml.cmd <- "pmml(crs$rpart)"
In the R console, executing the following code will export the C routine:
con <- file("dec tree.c", open="w")
cat(pmmltoc(toString(eval(parse(text=pmml.cmd))),
name="dec tree", includePMML=TRUE, includeMetaData="",
exportClass=FALSE), file=con)
close(con)
If you generate a pmml/XML file and want to export a C routine, you need to execute the following code lines with RStat open:
cat(pmmltoc(toString("dec tree.xml")
, "dec tree", TRUE, "", FALSE), file = "dec tree.c")| WebFOCUS | |
|
Feedback |