STDDEV: Calculating the Standard Deviation for a Set of Data Values
The STDDEV function returns a numeric value that represents the amount of dispersion in the data. The set of data can be specified as the entire population or a sample. The standard deviation is the square root of the variance, which is a measure of how observations deviate from their expected value (mean). If specified as a population, the divisor in the standard deviation calculation (also called degrees of freedom) will be the total number of data points, N. If specified as a sample, the divisor will be N-1.
If x¡ is an observation, N is the number of observations, and µ is the mean of all of the observations, the formula for calculating the standard deviation for a population is:
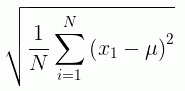
To calculate the standard deviation for a sample, the mean is calculated using the sample observations, and the divisor is N-1 instead of N.
Reference: Calculate the Standard Deviation in a Set of Data
STDDEV(field, sampling)
where:
- field
-
Numeric
Is the set of observations for the standard deviation calculation.
- sampling
-
Keyword
Indicates the origin of the data set. Can be one of the following values.
- P Entire population.
- S Sample of population.
Example: Calculating a Standard Deviation
The following request calculates the standard deviation of the DOLLARS field converted to double precision.
DEFINE FILE ibisamp/ggsales DOLLARS/D12.2 = DOLLARS; END TABLE FILE ibisamp/ggsales SUM DOLLARS STDDEV(DOLLARS,S) ON TABLE SET PAGE NOLEAD ON TABLE SET STYLE * GRID=OFF,$ ENDSTYLE END
The output is shown in the following image.
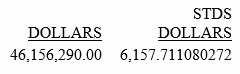
| WebFOCUS | |
|
Feedback |